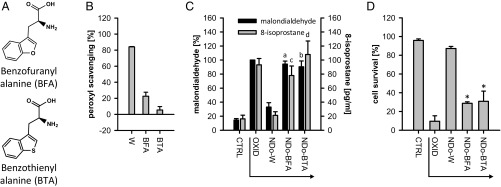
Fig. 4.
Specificity of W. (A) Chemical structures of BFA and BTA. (B) W, BFA, and BTA as scavengers of peroxyl radicals under conditions as in Fig. 3B (n = 3). (C) Inhibition of lipid peroxidation by NDo-W, NDo-BFA, and NDo-BTA under conditions as in Fig. 3D [malondialdehyde: F1 = 379, df = 1; F2 = 31, df = 12; aP < 0.001, bP < 0.001 versus “NDo-W” by post hoc test, n = 3 for compounds, n = 9 for controls; 8-isoprostane: F1 = 35, df = 1; F2 = 11, df = 12; cP = 0.014, dP = 0.001 versus “NDo-W” by post hoc test, n = 2 for compounds, n = 4 for controls (all from duplicates)]. (D) Survival of tBuOOH-treated fibroblasts in the presence of NDo-W, NDo-BFA, and NDo-BTA under conditions as in Fig. 3G (F1 = 511, df = 1; F2 = 48, df = 12; *P < 0.001 versus “NDo-W” by post hoc test, n = 3 for compounds, n = 9 for controls).