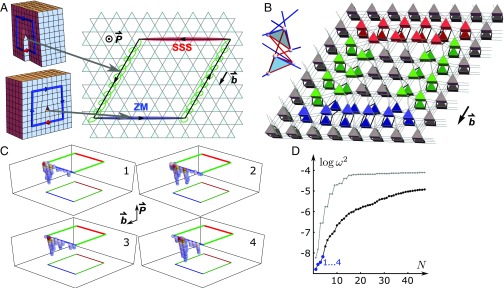
Fig. 4.
Dislocation loops can act as dipoles of topological charge. (A) Architectures of a dislocation loop in a periodic lattice: in a screw dislocation, the Burgers vector b is parallel to the dislocation line, whereas in an edge dislocation, the Burgers vector and the dislocation line are perpendicular. A dislocation loop can combine edge and screw dislocations along its contour. In a polarized lattice (with polarization P), a dislocation line separates in space an edge dislocation segment that carries zero modes (ZMs; blue) from an edge dislocation segment that carries states of self-stress [SSS; red; for example, via screw dislocations (green), which carry no such charges]. The net topological charge, defined as the difference between ZM and SSS, is zero when summed over a dislocation loop contour. Nevertheless, the dislocation loop carries a topological charge dipole, which is, in this example, parallel to the Burgers vector b. (B) Geometry of the dislocation loop. Each prism represents a unit cell with triangles oriented according to as shown in Inset. (C) Numerical results for the four lowest-frequency phonons (excluding the trivial translations) in a large ( unit cells) polarized lattice that has a dislocation loop: warmer color signifies a larger displacement within that unit cell. Plotted are only those unit cells that have displacements above a cutoff of 20% of the maximum. Note the localization of the softest modes to the near side of the loop in accordance with A and the polarization P. (D) The common logarithm of lowest mode frequencies for the th lowest mode plotted vs. , comparing two large samples (same size as C). The mode frequencies are significantly lower for the dislocated lattice (black) than in the nondislocated case (gray). Without a dislocation, the lowest eigenmodes are the extended plane-wave acoustic phonons, whereas with the dislocation, these modes include both the acoustic phonons and the modes localized along the dislocation loop (in blue, four lowest modes with eigenvectors that are plotted in C).