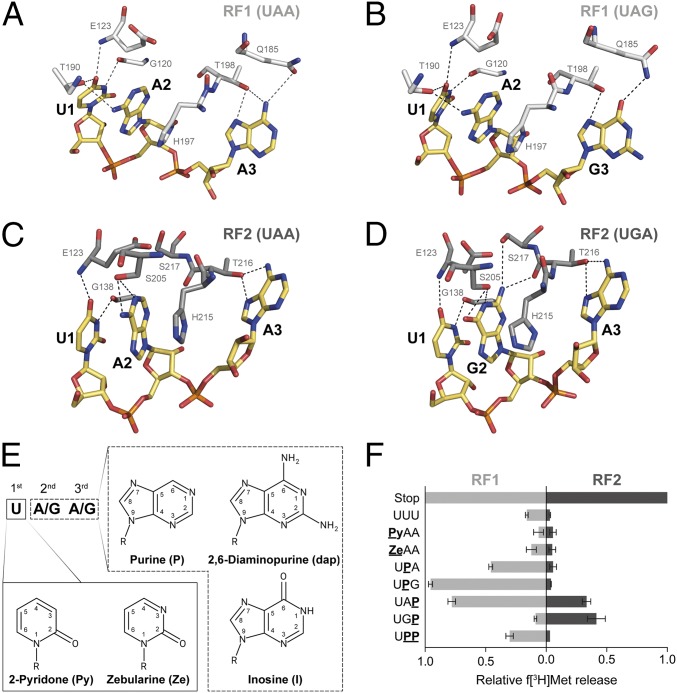
Fig. 1.
(A–D) Interactions between residues of bacterial RFs and the three stop codons at the decoding site. RF1 (white) and RF2 (gray) sense the stop codons (yellow) UAA (A) and UAG (B) or UAA (C) and UGA (D), respectively, by forming a set of hydrogen bonds (dashed lines; Escherichia coli numbering is used for RF residues; modified from refs. 32–35). (E) These interactions were modulated by the use of modified RNA bases within the stop codons. (F) The ability of RFs to recognize modified stop codons was determined by using a peptide release assay (error bars indicated SDs from the mean of three independent experiments).