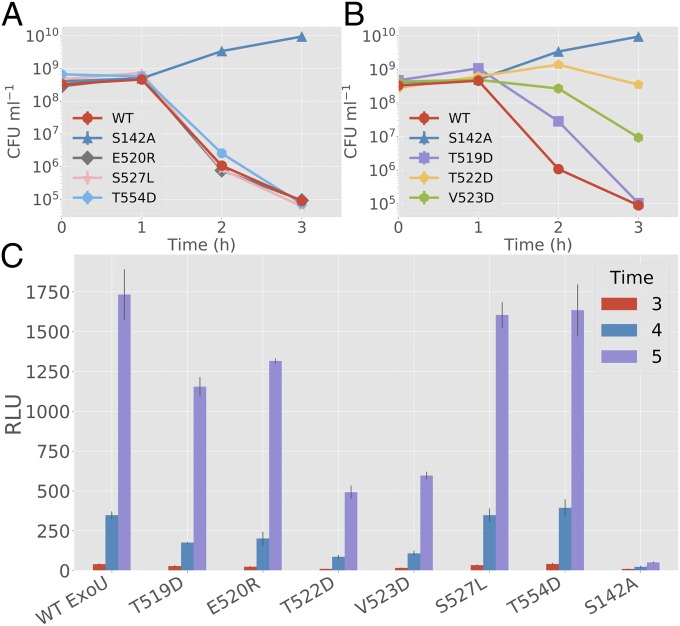
Fig. 4.
Biological activity of ExoU with bridging domain mutations. (A and B) Surrogate toxicity assays using E. coli strains coexpressing monoUb and ExoU variants. The y axis denotes colony-forming unit (CFU)/mL. (A) E520R, S527L, and T554D are compared with WT ExoU and S142A controls. No significant deviation from the parental ExoU control was detected (3-h time point). (B) T519D, T522D, and V523D are compared with WT ExoU and S142A controls. T522D and V523D demonstrate a significant difference (P < 0.001) from controls at 3 h. T519D shows a significant difference at hour 2 but not at hour 3, suggesting delayed toxicity. (C) Adenylate kinase release assays for HeLa cells infected with P. aeruginosa-expressing ExoU variants. S527L shows no significant deviation (P > 0.2) from WT and T554D controls at hour 5. Other mutations show a similar pattern to the E. coli dual-expression system, with T522D having the largest effect and E520R having the smallest. All experimental groups except for S527L are significantly different (P < 0.005) from both S142A and WT controls at hour 5. Error bars indicate SD about the mean of three independent data points. RLU, relative light unit.