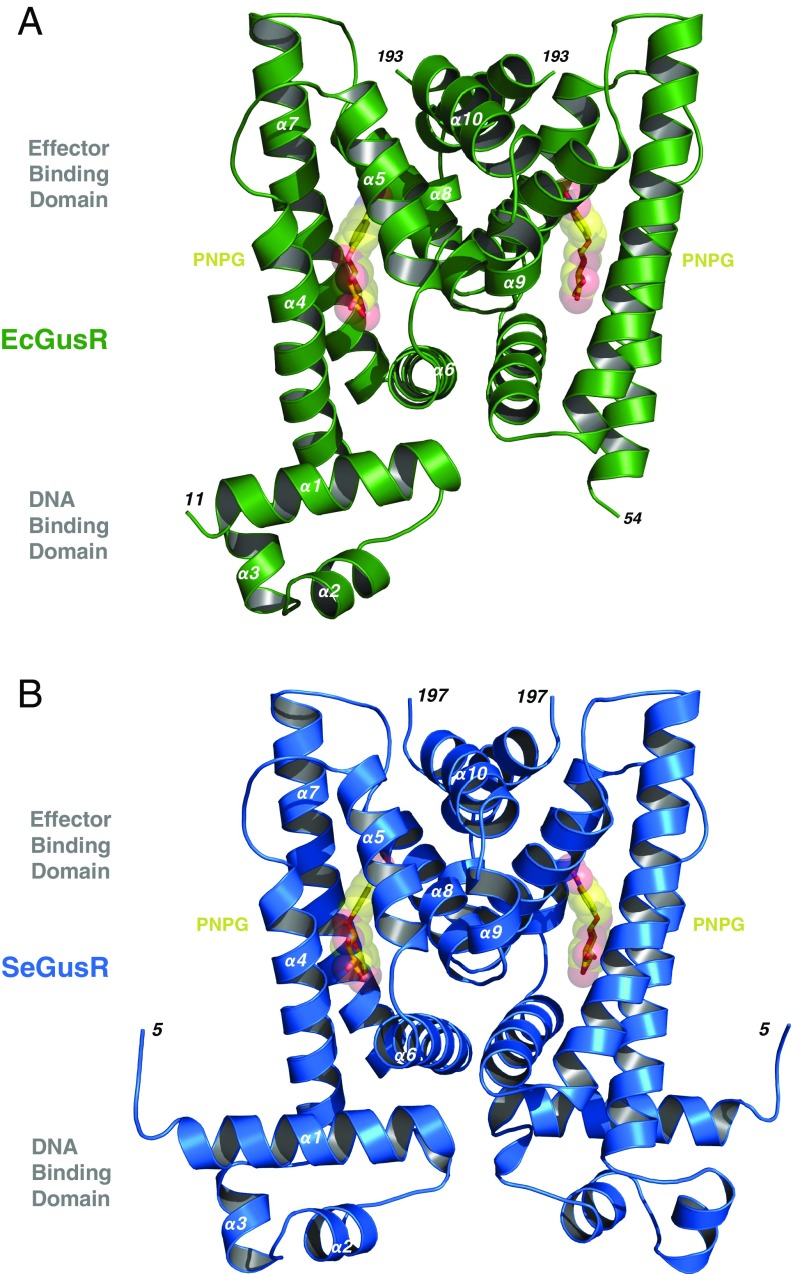
Fig. 2.
E. coli and S. enterica GusR crystal structures. (A) Ribbon representation of the 2.1-Å crystal structure of the EcGusR (green; PDB ID code 6AYI) homodimer bound to PNPG (yellow and red), revealing residues 11 to 193 in one monomer and residues 54 to 193 in the other monomer. EcGusR’s secondary structure is composed of 10 α-helices. The N-terminal DNA-binding domain is formed by α1 to α3, while the effector-binding domain is framed by α4 to α10. One E. coli GusR DBD is not visualized, likely due to motion within the crystal. (B) Ribbon representation of the 2.1-Å crystal structure of the SeGusR (blue; PDB ID code 6AYH) homodimer bound to PNPG (yellow and red) composed of residues 5 to 195 and intact DBDs and EBDs in both monomers.