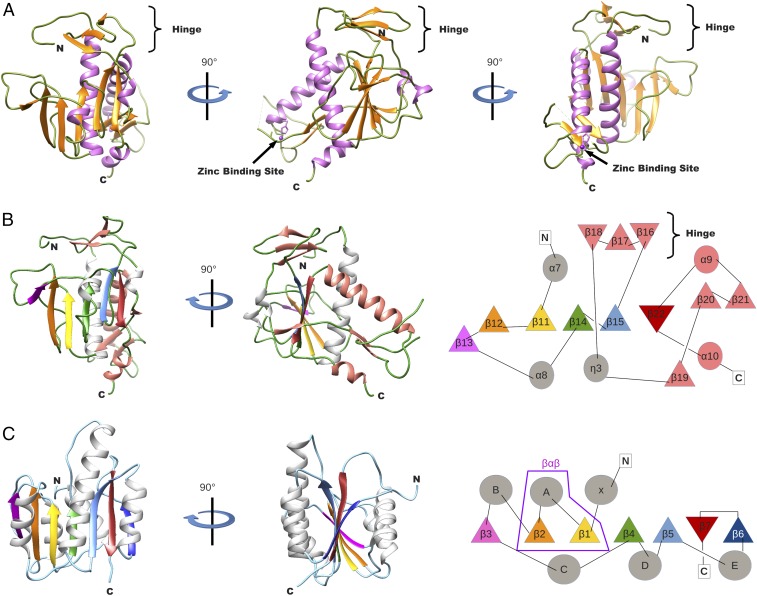
Fig. 3.
Structure model and topology of the nsp14 N7-MTase domain. (A) Ribbon model of the N7-MTase domain in three orientations (90° rotation apart) and colored by secondary structures as in Fig. 2A. The third zinc-binding site is shown with a zinc atom (purple sphere). (B) Organization analysis of the nsp14 N7-MTase domain. (Left) Ribbon model of the MTase domain in two orientations (of 90° rotation). Secondary structures are colored to highlight the topology: loop (green), α-helix (gray and salmon), and β-strand (purple, orange, gold, green, light blue, red, and salmon). (Right) Topology diagram of the nsp14 N7-MTase domain: β-strand (triangles) and α-helix (circles), with the corresponding secondary structures following the same color code as for the ribbon presentation. (C) Organization analysis of a canonical Rossmann fold FtsJ MTase (60). (Left) Ribbon model in two orientations (of 90° rotation), with the same color code as in B. (Right) Standard topology of MTase (so-called Rossmann fold). Secondary structures that align with those in the nsp14 N7-MTase domain have the same color as used in the B. The structural motif β-α-β defining the Rossmann fold is surrounded in purple.