Fig. 4.
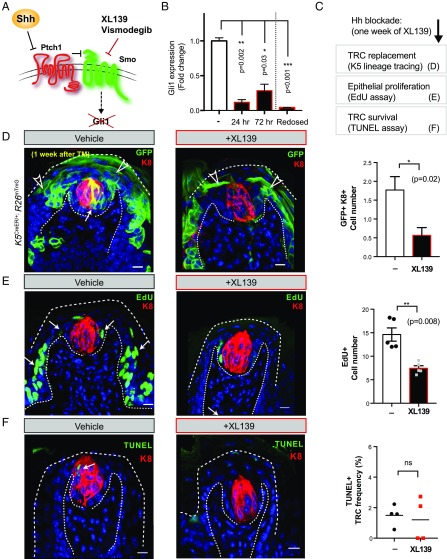
Hh blockade impedes TRC renewal by reducing epithelial cell proliferation and differentiation. (A) Diagram of Hedgehog signal transduction mechanism and usage of Smoothened antagonists Vismodegib (GDC-0449) and XL139 (BMS-833923) for Hh blockade, resulting in loss of downstream target Gli1 expression. (B) qRT-PCR analysis of Gli1 expression levels measured from isolated epithelial cells at indicated time points and normalized to the vehicle-treated group. The fourth bar (Redosed) denotes a group of mice from which Gli1 expression was measured 4 h after a second dose of XL139. (C) Experimental scheme. (D) Representative fungiform papillae from K5CreER/+;R26mTmG mice 1 wk after tamoxifen injection treated with vehicle or XL139. Note that K5-expressing lineage (GFP+) gives rise to TRCs (with GFP+K8+ double label; white arrow) and keratinocytes (with GFP+, single-label; open arrowhead). Panel, number of traced K5-lineage cells differentiating into GFP+K8+ double-positive cells per fungiform papilla (n = 26 vehicle- and 23 XL139-treated fungiform papillae; *P = 0.02). (E) Representative fungiform papilla 2 d after last dose of EdU (green, arrows) from mice treated with vehicle or XL139. Panel, number of EdU+ cells per fungiform papilla (n = 149 vehicle- and 118 XL139-treated; 5 mice in each group; **P = 0.008). (F) Immunofluorescence of TUNEL labeling (green) to detect apoptotic TRCs in fungiform papillae. Mice were treated with vehicle or XL139 for 7 d. Panel, frequency of TUNEL+ TRCs among total number of TRCs within each fungiform papilla (n = 56 vehicle- and 81 XL139-treated fungiform papillae from 3 or 4 mice in each group; ns, not significant). (Scale bars, 10 μm.)