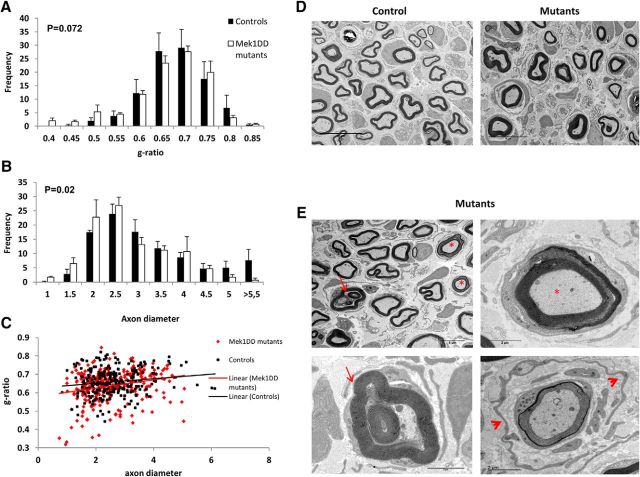
Figure 4.
MAPK/ERK activation in Schwann cells does not affect myelin thickness, but does affect myelin stability. A–C, Morphological analysis of MEK1DD mutant vs control sciatic nerve at 4 weeks postinjury was undertaken to determine the following: frequency distribution of g-ratio (A); frequency distribution of axon diameter (B); distribution graph of g-ratio in relation to axon diameter (C). D, TEM pictures of ipsilateral sciatic nerves from control and MEK1DD mutant mice, which illustrate that although myelin thickness does not change there are myelin defects shown in E: asterisks illustrate axons with myelin decompaction; arrows point to invaginating recurrent loops; arrowheads indicate supernumerary SC processes surrounding a myelinated axon with poorly compacted myelin that have the appearance of an early “onion bulb” structure. Error bars indicate SEM. n = 3 mice/group. Scale bars: D, 10 μm; E, top left, 5 μm; E, all other panels, 2 μm. Kolmogorov–Smirnov test performed.