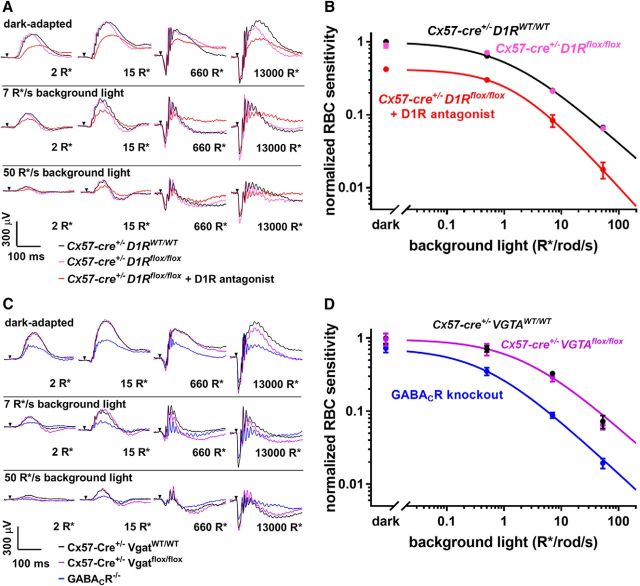
Figure 3.
Horizontal cells do not regulate rod bipolar cell sensitivity. A, Representative traces from ERG recordings of Cx57-Cre+/− D1RWT/WT mice, Cx57-Cre+/− D1Rflox/flox mice, and Cx57-Cre+/− D1Rflox/flox mice after intravitreal injection of a D1R antagonist SCH-23390. Conditions of dark or light adaptation and flash intensities are indicated in the panels. B, Rod bipolar cell sensitivity of Cx57-Cre+/− D1Rflox/flox mice and their Cx57-Cre+/− D1RWT/WT control littermates was determined in the dark and in the presence of three background illumination levels. Each sensitivity value was calculated as described in Materials and Methods, normalized to the dark sensitivity of control littermates and plotted as a function of background light. Light sensitivity of Cx57-Cre+/− D1Rflox/flox mice was similarly analyzed following intravitreal injection of D1R antagonist SCH-23390 and included for comparison. C, Representative traces from ERG recordings of Cx57-Cre+/− VGATWT/WT, Cx57-Cre+/− Vgatflox/flox, and GABACR knock-out mice. D, Rod bipolar cell sensitivity of Cx57-Cre+/− VGATflox/flox mice and their Cx57-Cre+/− VGATWT/WT control littermates was normalized to the dark sensitivity of control littermates and plotted as a function of background light. Rod bipolar cell sensitivity of GABACR knock-out mice was normalized to the dark sensitivity of the Cx57-Cre+/− VGATWT/WT mice and included for comparison. Animal types and pharmacological interventions used in each experiment are indicated and color-coded in the panels. Data from ≥12 eyes were averaged for each condition, except for the SCH-23390 injection experiment for which three eyes were analyzed. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.