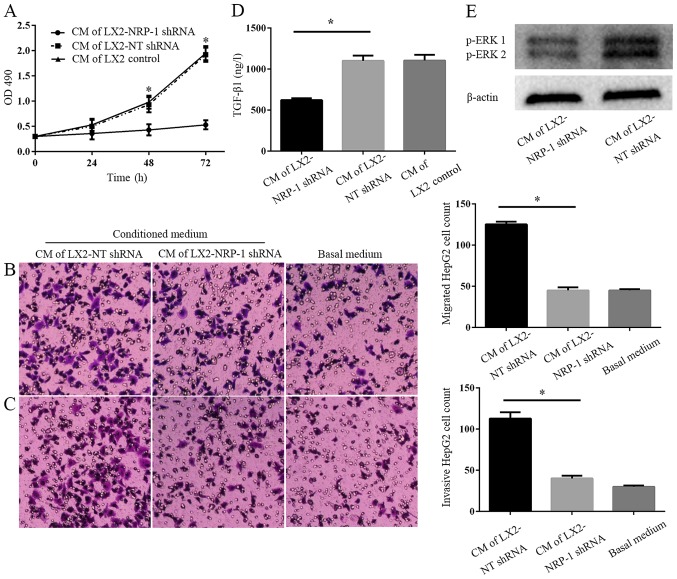
Figure 3.
NRP-1 knockdown impairs the effects of LX2 cells on tumor proliferation, migration and invasion in vitro. (A) CM were collected from control LX2 cells (transduced with NT shRNA lentiviruses) and NRP-1 knockdown LX2 cells (transduced with NRP-1 shRNA lentiviruses). HepG2 cells cultured in LX2 cells CM were subjected to MTT assay analysis. CM of NRP-1 knockdown LX2 cells was less effective in promoting HepG2 proliferation compared with that of control LX2 cells. *P<0.05 by analysis of variance; n=3 repeats with similar results. CM described in (A) was used as the chemoattractant in the Transwell chamber assays. CM of NRP-1 knockdown LX2 cells was less effective at promoting HepG2 (B) migration and (C) invasion in comparison with that of control LX2 cells. *P<0.05 by analysis of variance; n=3 repeats (magnification, ×100). (D) There was a markedly higher expression level of soluble TGF-β1 in CM from LX2-NT shRNA compared with LX2-NRP-1 shRNA CM (*P<0.05) as assessed by ELISA; n=3. (E) Western blot analysis using an antibody against phosphorylated ERK, p44 and p42, ERK1 and ERK2; n=3. CM, conditioned media; NT, non-targeting; shRNA, short hairpin RNA; NRP-1, neuropilin-1; ERK, extracellular signal-related kinase; OD, optical density; TGF-β1, transforming growth factor β1.