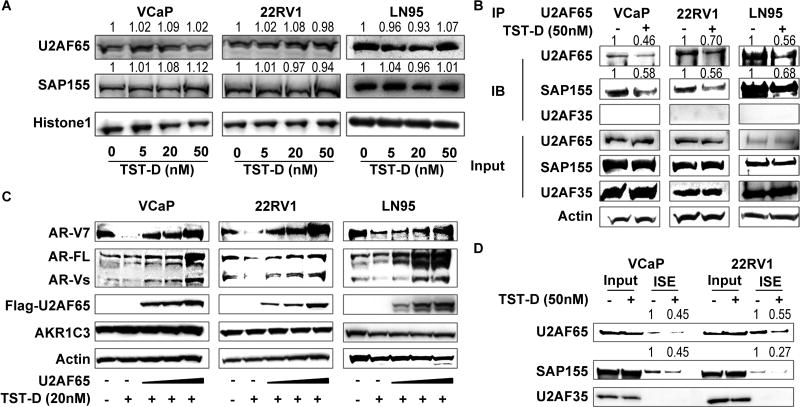
Figure 5. The mechanism of TST action on AR gene splicing.
(A) VCaP, 22RV1 and LN95 were treated with TST-D at 0, 5, 20, 50 nM for 24 hours; the expression of both U2AF65 and SAP155 proteins was analyzed by western blot. Histone 1 was used as the loading control. (B) 22RV1, VCaP and LN95 cells were pre-treated with 50 nM TST-D for 4 hours; total cell lysate were immunoprecipitated with U2AF65 antibodies plus protein G beads. Bound proteins were eluted and analyzed by western blot. (C) 22RV1, VCaP and LN95 cells were transiently transfected with mock vector or Flag-U2AF65 plasmid. Forty-eight hours after transfection, cells were treated with 20 nM TST-D for 4 hours. Both AR-V7 and AR-FL were analyzed by western blot. (D) 22RV1 and VCaP cell lysates were incubated with RNA oligos containing ISE. Oligo-associated factors were eluted and subjected to western blot for determining the interaction of splicing factor(s) with AR-V7 ISE.