FIGURE 2.
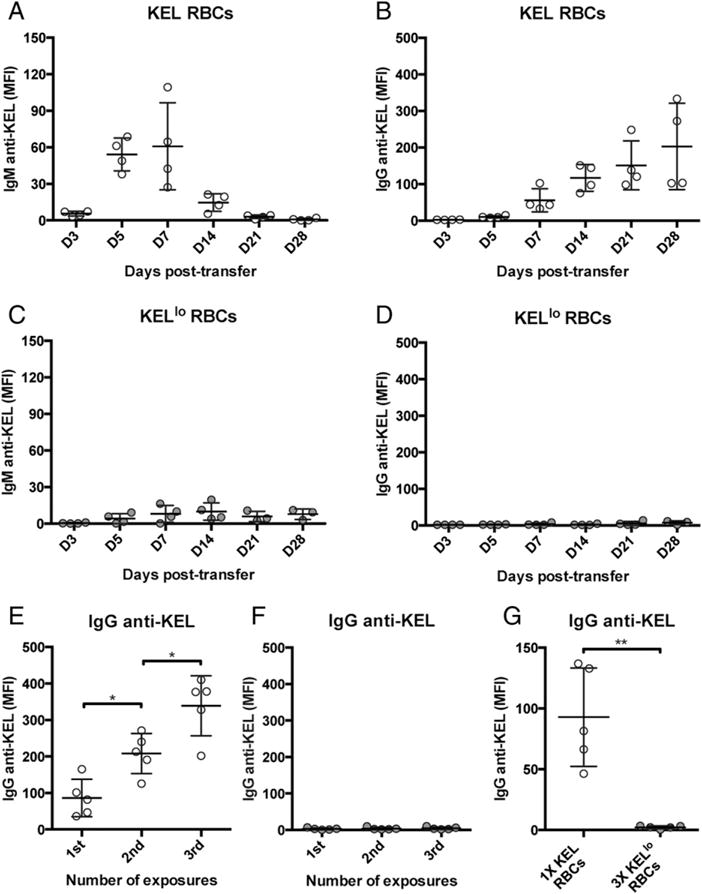
KELlo RBCs fail to induce detectable anti-KEL Abs. C57BL/6 recipients negative for the KEL Ag were transfused with KEL (A and B) or KELlo (C and D) RBCs, followed by serological detection for IgM anti-KEL or IgG anti-KEL at the time points indicated. C57BL/6 KEL− recipients were exposed to one, two, or three doses of KEL (E) or KELlo (F) RBCs, followed by examination of IgG anti-KEL Ab formation at day 14 posttransfer. (G) C57BL/6 KEL− recipients were exposed to a normal dose of KEL RBCs or three times the normal dose of KELlo RBCs, followed by evaluation of IgG anti-KEL Abs at day 14 posttransfer. Error bars indicate SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, one-way ANOVA.
