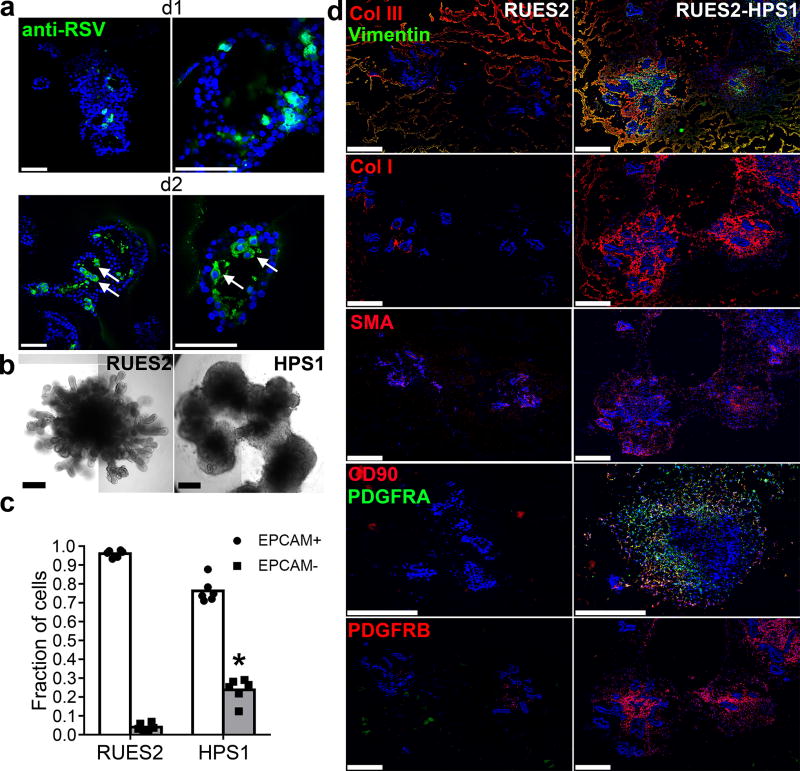
Figure 5. Potential application of LBOs in modeling human diseases.
(a) Confocal images of whole mount d170 LBOs 1 and 2 days after infection with RSV and stained using anti-RSV (all antigens) antibody. Arrows: infected cells in the lumen. Representative of 3 independent experiments. Scale bars 100 µm. (b) Bright field images of d50 LBO-derived Matrigel colonies from RUES2 and RUES2-HPS1 cells. Representative of six independent experiments. Scale bars 500 µm. (c) Fraction of EPCAM+ and EPCAM− cells in d50 LBO-derived colonies in 3D Matrigel cultures of RUES2 and RUES2-HPS1 cells. (n=6, mean±s.e.m of 3 technical replicates from two experiments; * P<0.0001; two-tailed Student’s t-test). The source data can be found in Supplementary Table 4. (d) Immunofluorescence staining for mesenchymal markers and ECM components in 3D Matrigel cultures of RUES2 and RUES2-HPS1 cells. Representative of 3 independent experiments. Scale bars 500 µm.