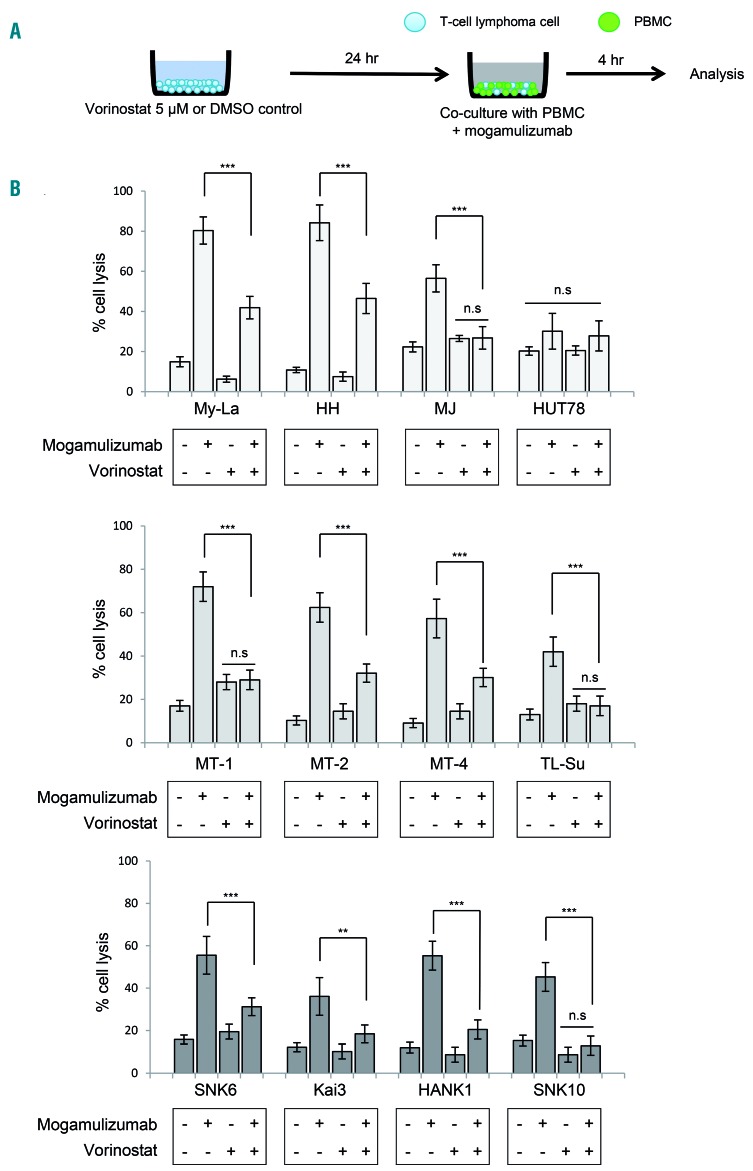
Figure 3.
Pretreatment of vorinostat significantly decreases mogamulizumab-induced antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Bars indicate the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) of three independent experiments. Asterisks (*) indicate statistical significance: **0.001 ≤ P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, n.s: not siginificant. (A) A schematic illustration of the ADCC assay is shown. Cells were treated with 5 μM vorinostat for 24 h or dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) as a control before mogamulizumab treatment. Cytotoxicity was measured using the lactate dehydrogenase assay in the presence of effector cells (peripheral blood mononuclear cells. PBMC) obtained from healthy volunteers and mogamulizumab (10 mg/mL) or the same volume of solvent (control). The ratio of target:effector cells was fixed at 1:50. (B) The ADCC assay against CTCL (upper panel: MyLa, HH, MJ, and HUT78), ATLL (middle panel: MT-1, MT-2, MT-4, and TL-Su), and NK/T-cell lymphoma (lower panel: SNK6, Kai3, HANK1, and SNK10) cell lines. x-axis: cell lines; y-axis: percent cell lysis.