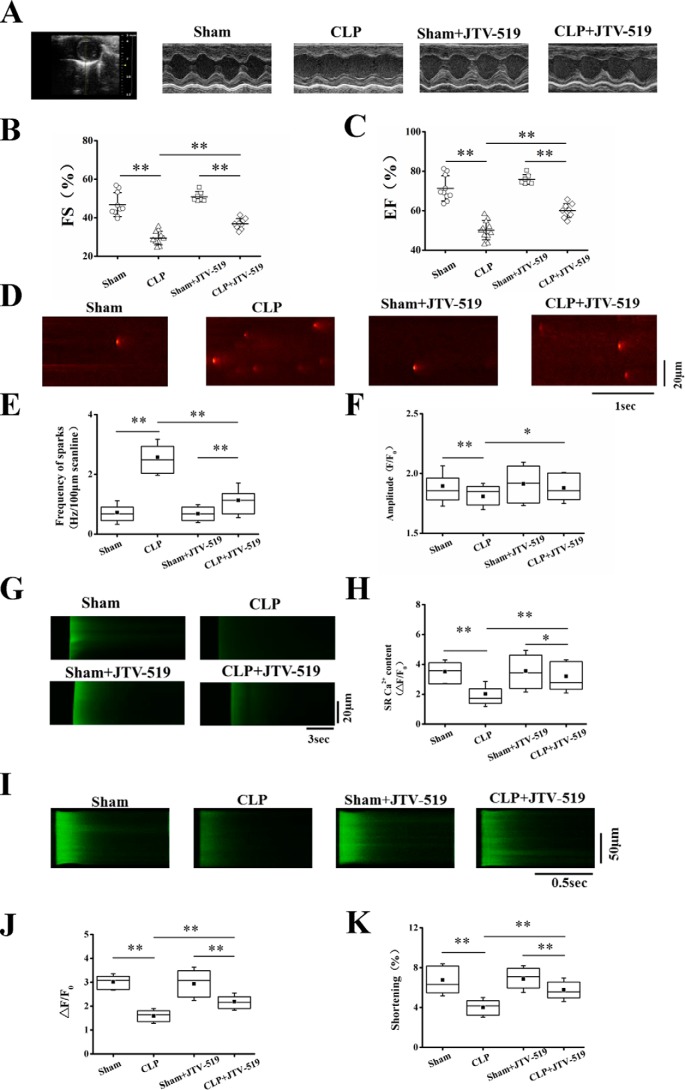
Figure 4.
JTV-519 prevented Ca2+ spark–mediated SR Ca2+ leak and increased cardiac function in septic mice. A mouse model of polymicrobial sepsis was produced by CLP. A, representative images generated by echocardiography in sham and septic mice with or without JTV-519 treatment. JTV-519 (0.5 mg/kg/h) was applied intraperitoneally 2 h before the surgery. B and C, quantification of LV FS (B) and LV EF (C) in four groups (n = 7–13 in each group). D, representative images of Ca2+ spark in cardiomyocytes isolated from sham or septic mice with or without JTV-519 treatment. JTV-519 (1 μm) was incubated with sham or septic cardiomyocytes for 1 h before measurement of the Ca2+ spark, SR Ca2+ content, systolic Ca2+ transient, and cell shortening. E and F, statistics of the frequency and amplitude of Ca2+ sparks (n = 40–51 cells in each group). G, representative images of caffeine-elicited Ca2+ transient in cardiomyocytes isolated from sham or septic mice with or without JTV-519 treatment in vitro. H, statistics of the amplitude of caffeine-elicited Ca2+ transient (SR Ca2+ content; n = 24–28 cells in each group). I, representative confocal line-scan images of field stimulation (1 Hz)-induced Ca2+ transient in four groups. J and K, statistics of the amplitude of the systolic Ca2+ transient (J) and the maximum of cell shortening (K; n = 50–79 in each group). *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01. Error bars, S.D.