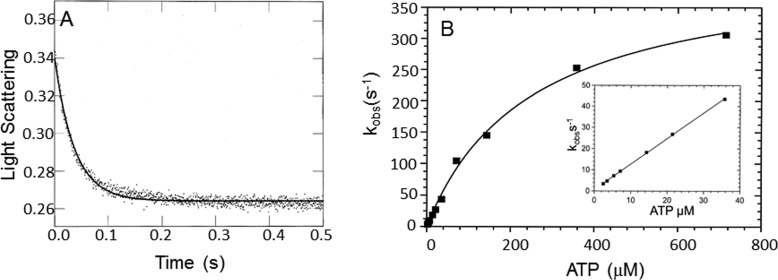
Figure 6.
Dissociation of myoVIIa-sh1 from actin upon ATP binding. Experimental conditions in the cell were as follows: actomyoVIIa-sh1 (0.7 μm myosin + 1.4 μm actin) and 3.5 μm CaM, 0.72–715 μm ATP, 25 mm KCl, 10 mm MOPS, 3 mm MgCl2, 1 mm EGTA, pH 7.5, 20 °C. A, the decrease in light scattering was observed upon mixing actomyosin VIIa-sh1 with MgATP. Three traces for each ATP concentration were averaged and fit to a single exponential equation. A representative trace at 21.5 μm ATP yielded I(t) = 0.13e−26.8 + C. B, the dependence of kobs upon ATP concentration was fit to a hyperbola, resulting in a maximal kobs of 420.4 ± 17.4 s−1 and a Kapp = 293 ± 23.5 μm. Inset, data from 0–50 μm ATP. The rate of ATP binding to actomyosin calculated from the initial slope is 1.2 ± 0.01 μm−1 s−1.