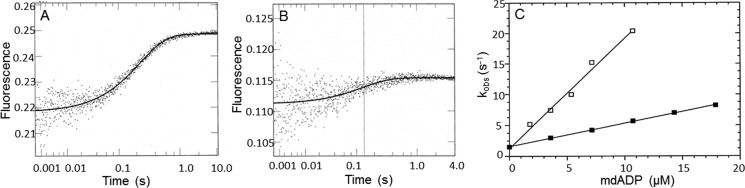
Figure 7.
Kinetics of dmantADP binding to myoVIIa-sh1 and actomyoVIIa-sh1. 1.2 μm myoVIIa-sh1 (A) or 1.2 μm myoVIIa-sh1 + 2.4 μm actin (B) was mixed with dmantADP in single mixing stopped-flow fluorescence experiments. Experimental conditions were as follows: 25 mm KCl, 10 mm MOPS, 6 μm calmodulin, 3 mm MgCl2, 1 mm EGTA, pH 7.5, 20 °C. A, shows the average of three traces of the stopped-flow recording of 1.2 μm myoVIIa-sh1 binding to 7.2 μm dmantADP. The solid line was fit to a single exponential equation, resulting in a kobs of 4.2 s−1. B, average of three traces of the stopped-flow recording of 1.2 μm actomyosin VIIa-sh1 binding to 3.6 μm dmantADP. The solid line was best fit to a single exponential equation with a kobs of 7.4 s−1. C, experimental conditions are the same as in A and B except that 1.2 μm myoVIIa-sh1 or 1.2 μm actomyoVIIa-sh1 was mixed with increasing concentrations (3.6–17.8 μm) of dmantADP. The second order rate constant for dmantADP binding (kD) to myoVIIa-sh1 was 0.4 ± 0.04 μm−1 s−1, and the value for binding to actomyoVIIa-sh1 (kAD) was 1.8 ± 0.08 μm−1 s−1. The rate of ADP dissociation calculated from the intercept was 1.6 ± 0.43 s−1 for myosin VIIa-sh1 and 1.8 ± 0.2 s−1 for actomyosin VIIa-sh1.