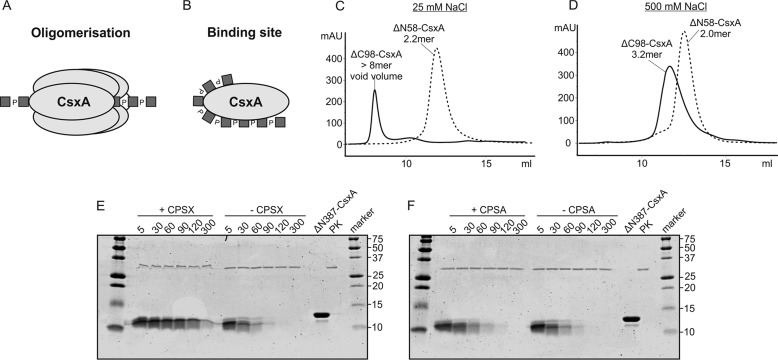
Figure 4.
The C terminus of CsxA contains an extended product-binding site. Two models exist in literature that may explain the role of the CsxA C-terminal domain in mediating processivity. A, elements in this domain promote the formation of an oligomeric structure that encloses the growing CPS chain. B, the C terminus harbors a second CPS binding site. C and D, in size-exclusion chromatography the oligomeric state of the truncated CsxA constructs was determined under low-salt (C) and high-salt (D) conditions. Although the C-terminally truncated protein eluted very similar to wild type (21), the protein formed an apparent dimer after removal of the N-terminal 58 amino acids. E and F, proteinase K sensitivity of the isolated C-terminal domain (ΔN387-CsxA) was assayed in the presence and absence of CPSX (E) and CPSA (F). The delayed degradation of the protein in the presence of CPSX but not CPSA argues for a specific binding of the first. As control, the purified ΔN387-CsxA and proteinase K (PK) were loaded onto the gel.