Figure 6. Relevance of CXCR4 pathway expression to human atherosclerotic disease.
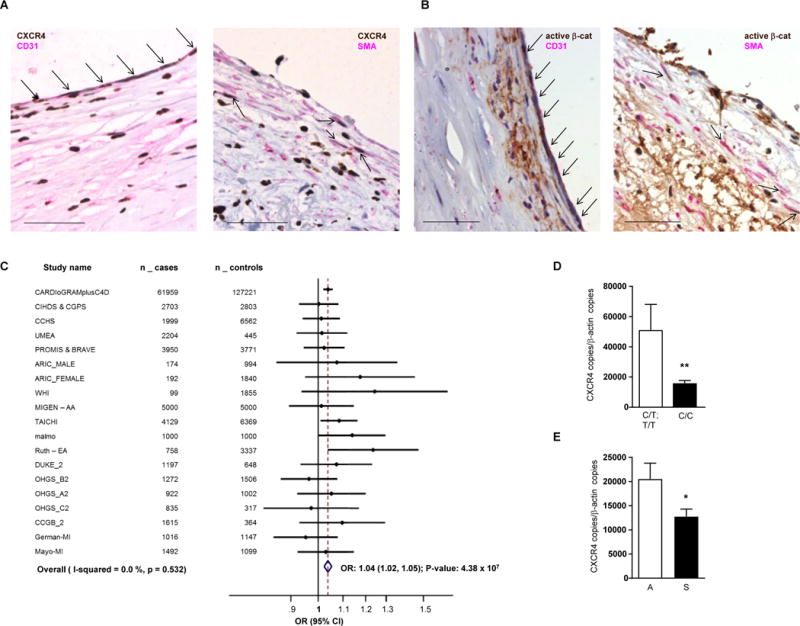
(A) Staining of CXCR4 in human atherosclerotic lesions. Human carotid endarterectomy specimen were stained for CXCR4 (brown) in combination with CD31 (left, pink) or SMA (right, pink). Scale bar = 50 µm. Arrows indicate CXCR4+ ECs (left) or CXCR4+ SMCs (right). (B) Staining for active β-catenin in human atherosclerotic lesions. Human carotid endarterectomy specimen were stained for active β-catenin (ABC; brown) in combination with CD31 (left, pink) or SMA (right, pink). Scale bar = 50 µm. Arrows indicate ABC+ ECs (left) or ABC+ SMCs (right). (C) Forest blot for the associations of CHD risk with rs2322864. We examined the association of 345 common variants at the CXCR4 locus (± 25KB) with CHD by using data on 92,516 CHD cases and 167,280 controls (see Supplemental Table 4 for details of data sets included), most notably interrogating the CARDIoGRAMplusC4D data. We conducted fine-mapping studies in 12,500 myocardial infarction cases and 12,000 controls and genotyped all 512 variants with a minor allele frequency >0.1% identified by the 1000-Genomes project at the CXCR4 locus. A P-value of 5×10−5 was considered as statistically significant based on Bonferroni correction for 857 variants. Odds ratio (OR) with 95% confidence interval (CI) and P-value are given. The C-allele at rs2322864 was found to be associated with increased CHD risk (OR: 1.04; P=4.38×10−7). (D) Association of rs2322864 with CXCR4 expression in carotid endarterectomy specimen (C/T; T/T: n=121 and C/C: n=67, Mann-Whitney test with Bonferroni correction to adjust for multiple comparisons). (E) Correlation of CXCR4 expression with clinical carotid stenosis, as evident by neurologic events, e.g. transient ischemic attacks (A, asymptomatic, n=25; S, symptomatic, n=19, unpaired t-test with Welch correction); CXCR4 expression was normalized to β-actin expression (mean±SEM). *P<0.05.
