Figure 2.
Location of Identified Variants in FZD2 Segregating with the Associated Phenotypic Features
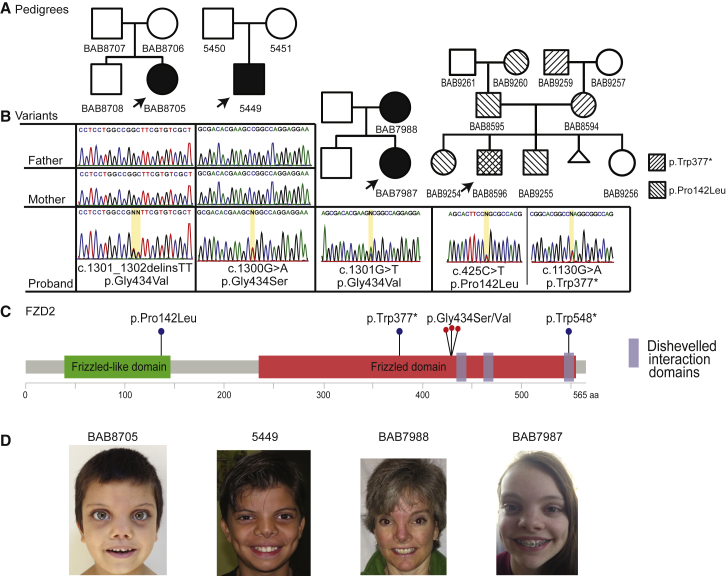
(A) Pedigrees of the four probands with Robinow syndrome features, carrying variants in FZD2.
(B) Sanger sequencing traces for index case subjects, demonstrating the detected variants at the nucleotide level. Family of BAB8596, far right, contains two variants in FZD2: p.Trp377∗ and p.Pro142Leu. The stop gain was inherited from an affected mother and the missense represents a variant of uncertain significance inherited from father.
(C) Representation of the known functional domains of FZD2 (green and red rectangles).86 Location of protein-coding variants identified in our cohort: one stop gain and three recurrent variants all affecting glycine 434 located within the third intracellular loop (red dots). One additional variant (p.Trp548∗) from the literature, and reported in association with omodysplasia, is also included.46
(D) Photographs of consenting subjects with FZD2 variants demonstrating shared facial characteristics consisting of a high, broad forehead, prominent eyes, broad and low nasal bridge, low-set ears, broad nasal tip, and anteverted nares.