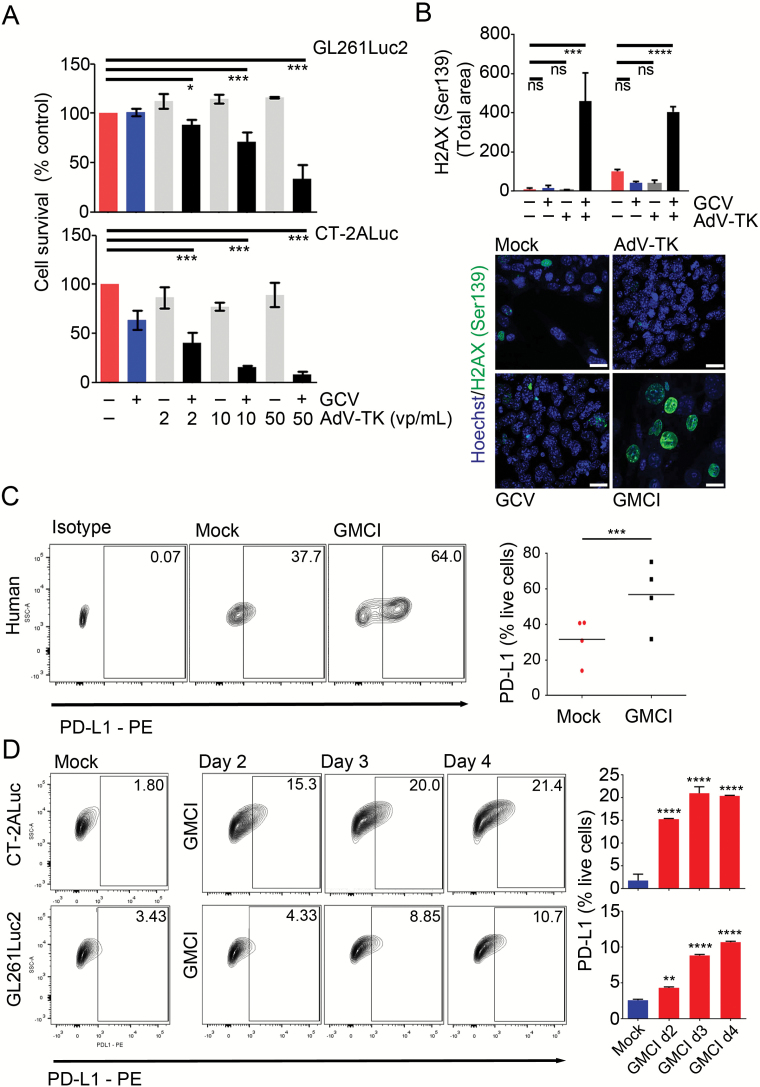
Fig. 1.
Cytotoxic effects and PD-L1 induction by GMCI in glioblastoma cell lines in vitro. (A) Mouse glioblastoma cell lines were transduced with AdV-tk at the indicated concentration and treated with 10 μg/mL of GCV/day for 4 days. Cytotoxicity was determined by the Presto blue (MTT) assay after 6 days treatment. (B) H2AX Ser139 quantification of 2 mouse glioblastoma cell lines (GL261Luc2 and CT-2ALuc) after AdV-tk, GCV, and GMCI treatments compared with mock 4 days after treatment. Confocal microscopic images of CT-2ALuc cells after AdV-tk, GCV, and GMCI treatments showing nuclear staining with phospho-histone H2AX (Ser139) in green and Hoechst in blue. Scale bars: 20 µm. (C–D) Human glioblastoma stemlike cells (hGSCs, G33, G35, G146, and G157) and mouse glioblastoma cell lines were infected with 10 vp/μL AdV-tk, and 10 μg/mL GCV was added daily for 4 days. (C) Representative flow cytometry contour plots from one human GSC (G35) (left) and aggregate plots from 4 human GSCs (right). (D) PD-L1 expression in mouse glioblastoma cell lines after GMCI compared with mock. Flow data are shown for CT-2ALuc cells (left). Graph shows a time-dependent increase in PD-L1 cell surface expression in CT-2ALuc and GL261Luc2 cells (right). One-way ANOVA was used to determine statistical significance (***P ≤ 0.001, **P ≤ 0.01, *P ≤ 0.05, ns, not statistically significant).