Figure 1.
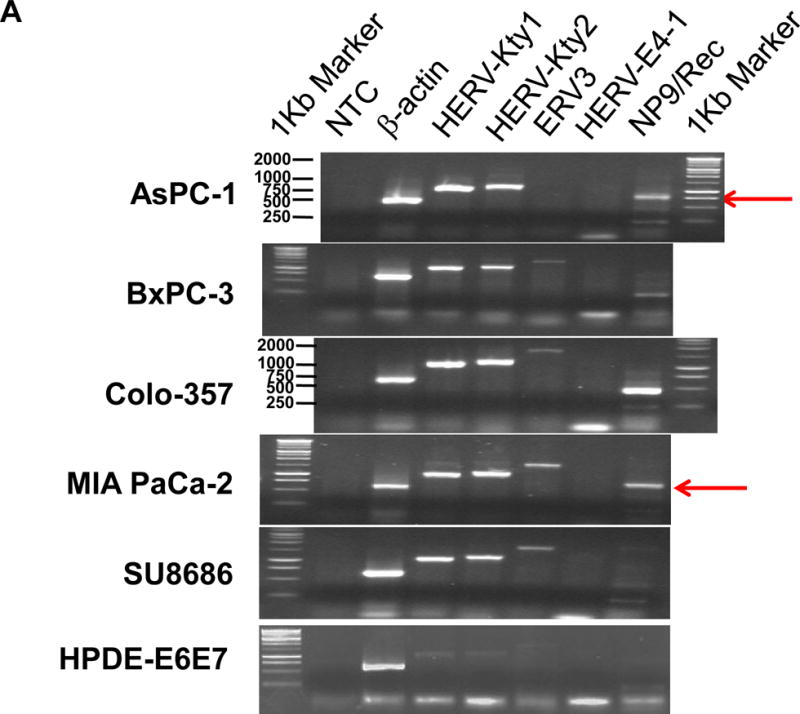
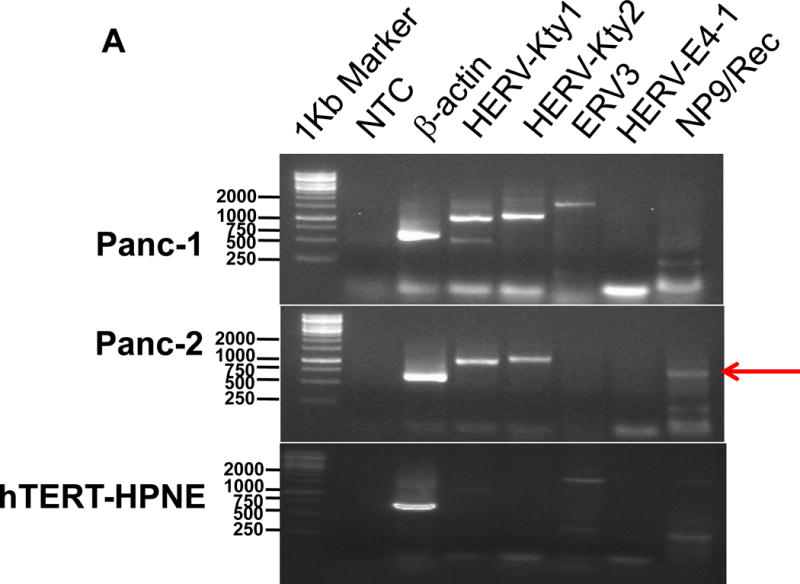
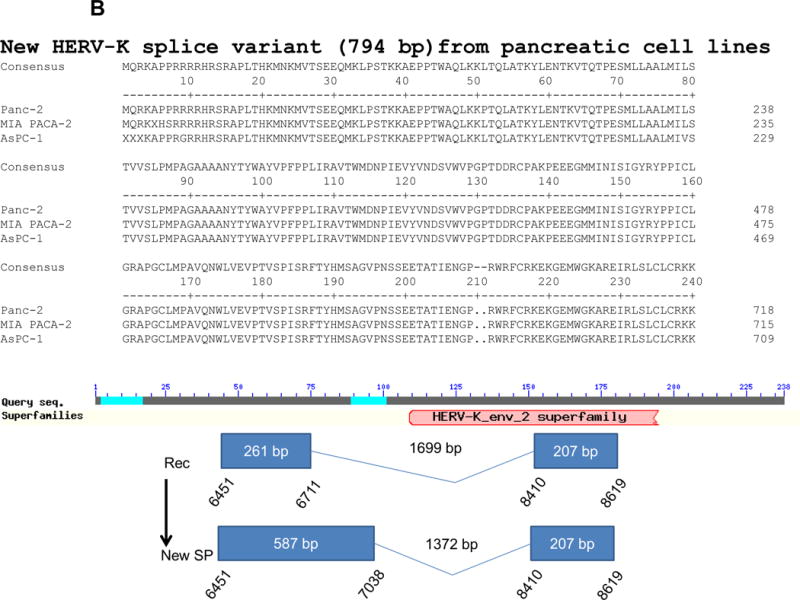
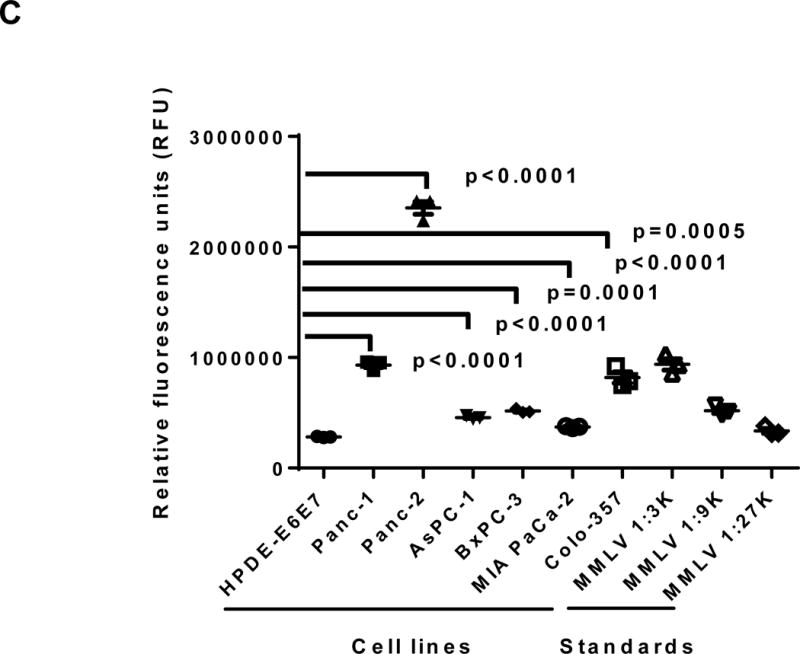
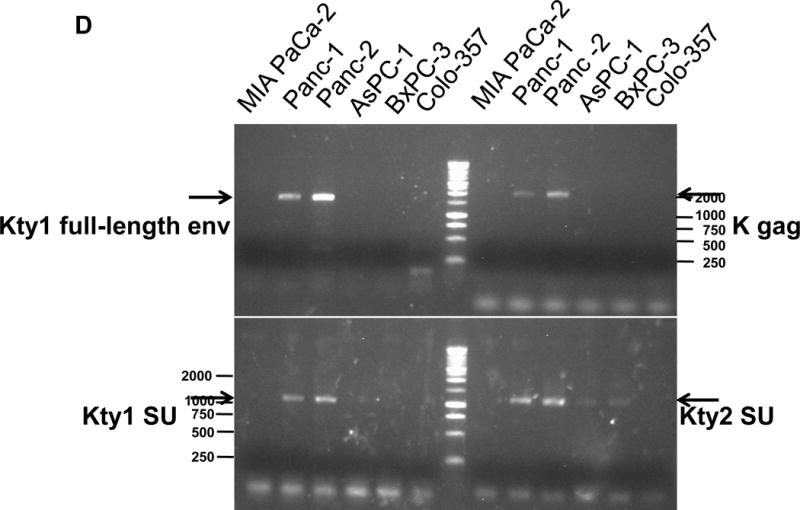
Expression of human endogenous retroviruses and viral reverse transcriptase activity in pancreatic cancer cells and tissues. A, the expression of various HERV env mRNAs was evaluated in pancreatic cell lines by RT-PCR using corresponding primer pairs. NTC: no template control; β-actin: positive control. HERV-Kty1: type 1 HERV-K env SU (1,104 bp); HERV-Kty2: type 2 HERV-K env SU (1,194 bp); ERV3: ERV3 env, HERV-E4-1: HERV-E env; NP9/Rec: transcripts amplified using NP9 primers. A new HERV-K splice variant (794 bp) present in several PC cell lines is shown (red arrow). β-actin was used as housekeeping gene. B, the predicted amino acid composition of the HERV-K splice variant from several PC cell lines is shown. Furthermore, the splice donor and acceptor of the new HERV-K splice variant was compared with splice donors and acceptors of Rec (HERV-K113; AY037928.1). C, reverse transcriptase (RT) activity was compared in gradient fractions prepared with a 50% iodixanol cushion from cell culture media (200 ml) of various pancreatic cell lines. Relative florescence units (RFU) in various pancreatic cell lines were compared. Serial dilutions (1:3,000, 1:9,000, and 1:27,000) of MMLV RT (Stratagene) were used as calibrators (standards). Student’s t-test was used to find statistically significant differences in RT activity between each PC cell line compared with HPDE-E6E7 cell line. D, vRNAs were isolated from gradient fractions of PC cell culture media, and expression of HERV-K genes [HERV-K full-length env and gag, HERV-K type 1 SU RNA (Kty1SU), and HERV-K type 2 SU RNA (Kty2 SU)] was determined by RT-PCR using specific primers. The higher expression of vRNAs in Panc-1 and Panc-2 cells matched the RT activities in their culture media.
