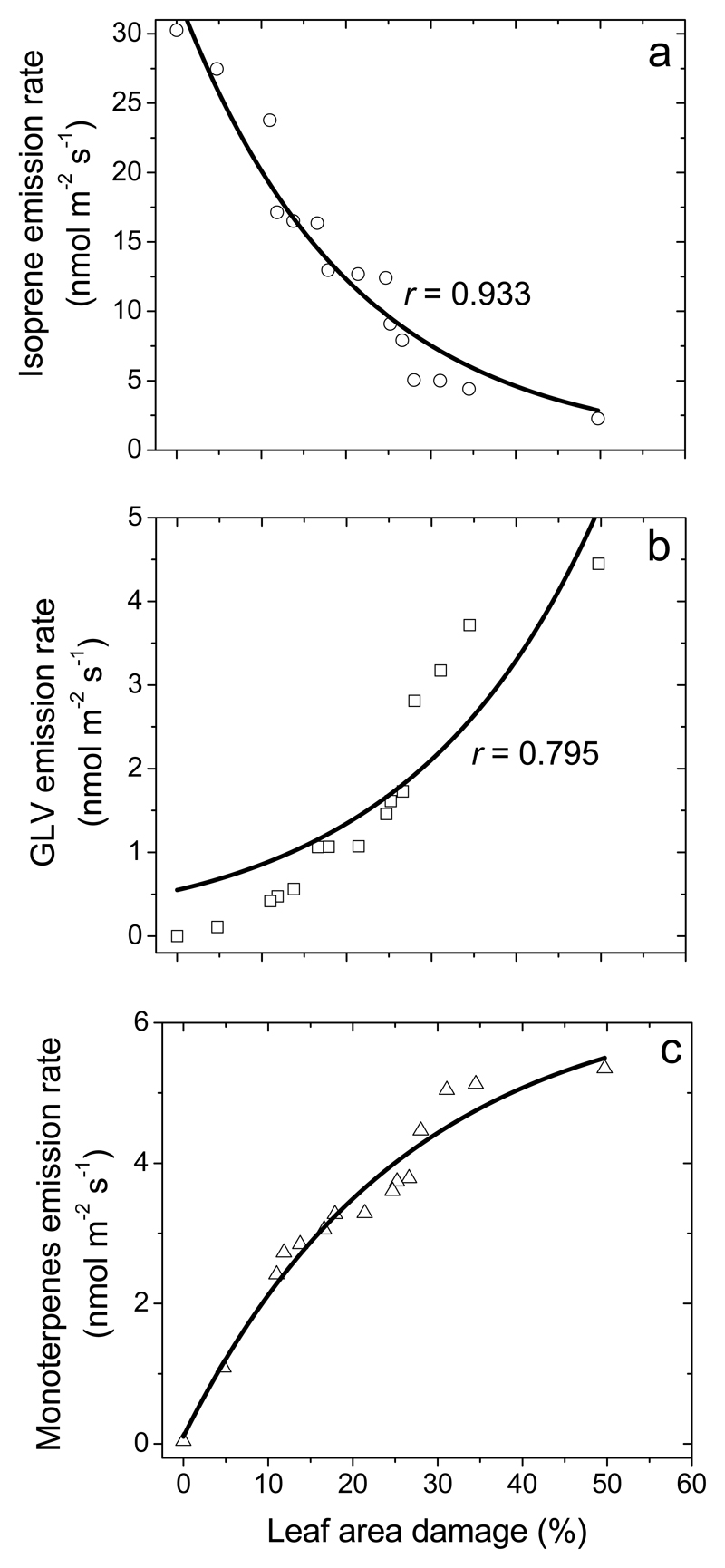
Fig. 2.
Emissions rates of isoprene (a), green leaf volatiles (b; GLV, volatiles of lipoxygenase pathway, LOX volatiles) and monoterpenes (c) from Q. robur leaves with different degrees of feeding by L. dispar larvae (replicates and data presentation as in Fig. 1). Total LOX product emission was calculated as the sum of emissions of 1-hexanol, (Z)-3-hexenol, (Z)-2-hexenal, and (Z)-3-hexenyl acetate and the total monoterpene emission as the sum of emissions of α-pinene, β-pinene, camphene, limonene, Δ-3-carene, p-cymene, and β-phellandrene. Data were fitted by non-linear regressions in the form of y = abx.