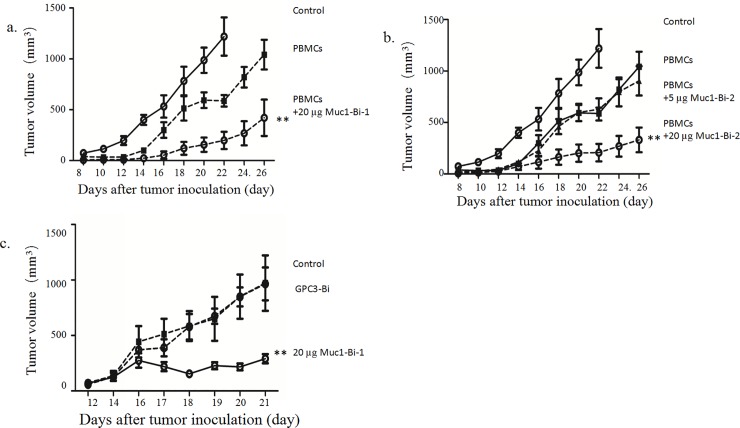
Fig 7. Muc1-Bi-1 and Muc1-Bi-2 inhibit tumor growth in vivo.
NOD/SCID mice (n = 7/group, female) were engrafted subcutaneously with LS174T cells (1×106 cells/mice) (circle, solid line) with or without freshly isolated human PBMCs (5×106 cells/mice). The mice were then treated with Muc1-Bi-1 (20μg/mouse), or Muc1-Bi-2 (5 and 20μg/mouse) as described in the Materials and Methods. For the mice transplanted with LS174T and PBMCs simultaneously, a). LS174T only (circle, solid line), LS174T with PBMCs (square, dash line), LS174T and PBMCs treated with Muc1-Bi-1 (20μg/mouse) (circle, dash line). b). LS174T only (circle, solid line), LS174T with PBMCs (square, dash line), LS174T and PBMCs treated with Muc1-Bi-2 (5μg/mouse) (triangle, dash line), Muc1-Bi-2 (20μg/mouse) (circle, dash line). c). PBMCs were transplanted after tumor size reaches 50–100 mm3, PBS (circle, solid line), GPC3 (square, dash line), Muc1-Bi-1 (20μg/mouse) (circle, dash line). The data represent the average tumor volumes of 6 mice. Error bars represent the standard deviation (**P< 0.01, t test, Muc1-Bi-1 and Muc1-Bi-2 (20μg) vs the other groups).