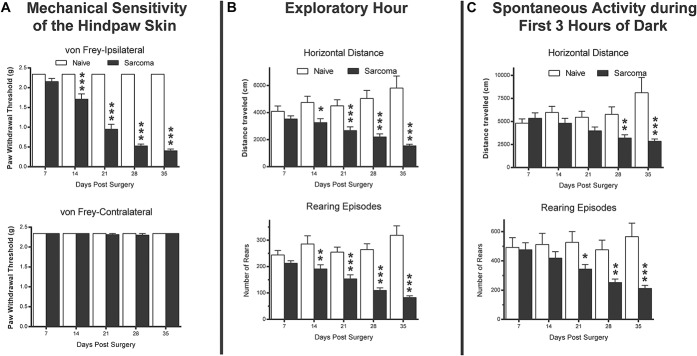
Figure 5.
Comparison between cancer-induced bone pain changes in mechanical hypersensitivity of the skin, initial daytime exploratory activity and spontaneous nighttime activity. Note that at day 35 post-tumor injection mechanical hypersensitivity of the skin shows a greater than 80% decline, whereas initial daytime exploratory activity declines by approximately 60% and spontaneous nighttime activity declines by approximately 50%. Also note that mechanical hypersensitivity of the skin is highly significant (P < 0.001) by day 14 post-tumor injection, whereas initial daytime exploratory activity only reaches this level of significance at day 21 post-tumor injection and spontaneous nighttime activity only reaches this level of significance at day 35 post-tumor injection. Significance in differences between animals with bone cancer vs naive controls is indicated by *, **, *** = P < 0.05, 0.01 and 0.001, respectively. (A) P values represent the comparison of naive vs sarcoma on difference scores in skin sensitivity (contralateral minus ipsilateral for each animal) for each day.