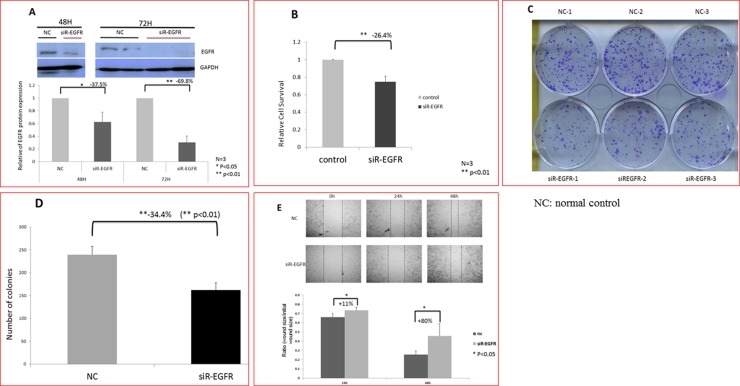
Figure 1. Reduced the proliferation rate and migration ability of human cancer cells (Caco-2) caused by EGFR knockdown.
(A) Western blot results showing that the expression of EGFR decreased significantly after EGFR knockdown at 48 h (p < 0.05) and 72 h (p < 0.01). (B) The proliferation of Caco-2 cells decreased significantly after EGFR knockdown. EGFR knockdown exerted a significant antiproliferative effect (p < 0.01). (C and D) EGFR knockdown significantly reduced colony number of Caco-2 cells (p < 0.01). (E) The cell migration ability of Caco-2 cells decreased significantly after EGFR knockdown. After 48 h of incubation, the narrowest gap distances decreased significantly after EGFR knockdown. Therefore, EGFR knockdown significantly inhibited the migration of Caco-2 cells (p < 0.05).