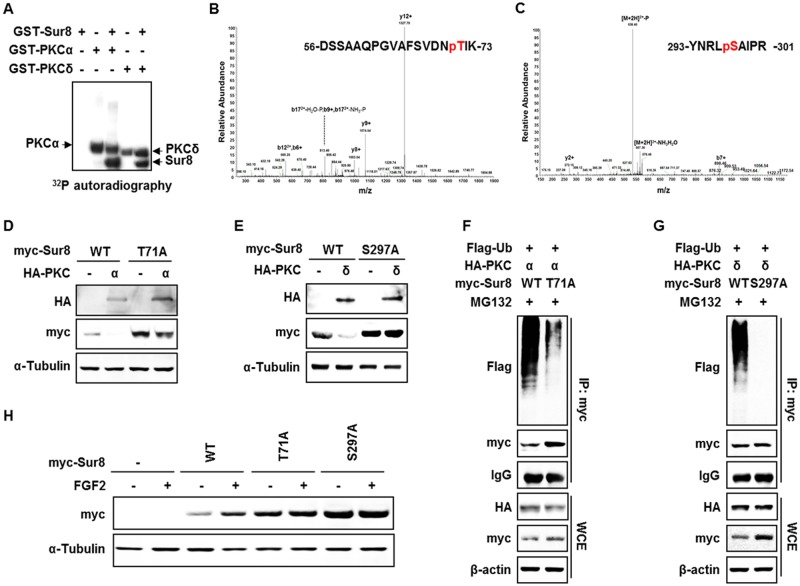
Figure 4. Phosphorylation of Sur8 at Thr71 and Ser297 by PKCα and PKCδ, respectively, are responsible for Sur8 degradation.
(A) Autoradiography of in vitro kinase assays with recombinant GST-Sur8, GST-PKCα, or GST-PKCδ alone, or GST-Sur8 plus GST-PKCα or GST-PKCδ. Autophosphorylated PKCα and PKCδ proteins, and phosphorylated Sur8 proteins are indicated. (B, C) Identification of phosphorylation sites of Sur8 by liquid chromatography tandem-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Graphs show representative mass spectrum of Sur8 depicting mass/charge (m/z) of identified PKCα (B) or PKCδ (C) phosphorylation sites. Spectra of the phosphopeptides in the digested Sur8 protein are shown. (D, E) Effects of nonphosphorylatable mutations of Sur8 on PKCα or PKCδ regulation of its stability. HEK293 cells were transfected with 1 μg of myc-Sur8-WT, myc-Sur8-T71A or myc-Sur8-S297A plasmid with or without HA-PKCα (D) or HA-PKCδ (E) plasmid. (F, G) Nonphosphorylatable mutation of T71 or S297 reduces Sur8 ubiquitination. Cells were transfected in the combinations of plasmids as indicated, followed by MG132 treatment for 4 hours before WCEs were immunoprecipitated with anti-myc antibody. (H) Cells were transfected with Sur8 nonphosphorylatable mutants and treated with FGF2 as indicated. WCEs were subjected to immunoblot analysis using the indicated antibodies (D-H).