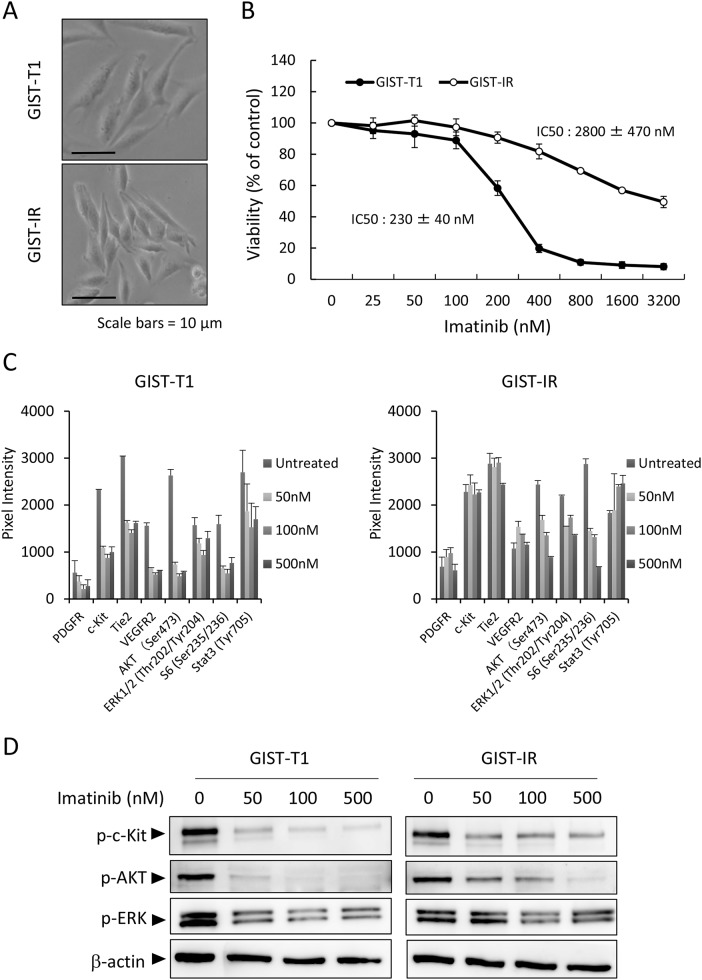
Figure 1. Characterization of the imatinib-resistant GIST cell line, GIST-IR.
(A) The appearance of imatinib-resistant GIST cells, GIST-IR cells, shows a spindle-like shape without obvious morphological changes from the parental cell, GIST-T1 cells. (B) 5.0 × 103 GIST-T1 or GIST-IR cells were plated in 96-well plates and cultured with imatinib (25 - 3200 nM). After 48 hours, cell viability was measured by WST-8 assay. Imatinib showed efficacy against GIST-T1 and GIST-IR cells with IC50s of 230 ± 40 nM and 2800 ± 470 nM, respectively. (C) Expression of activated tyrosine kinase receptors and downstream signals in GIST-T1 and GIST-IR cells, and the effect of imatinib on their phosphorylation status were evaluated using RTK signaling antibody array. Bar graphs represent the quantified receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) signaling antibody array images. Results represent the mean ± SD of three experiments performed in triplicate. (D) Protein extract from GIST-T1 and GIST-IR cells incubated in culture media supplemented with the indicated concentration of imatinib for 48 hours was immunoblotted with anti-c-Kit (Tyr719), anti-phospho-AKT (Ser473), anti-phospho-ERK1/2 (Thr202/Tyr204). β-actin is shown as a loading control.