Figure 1.
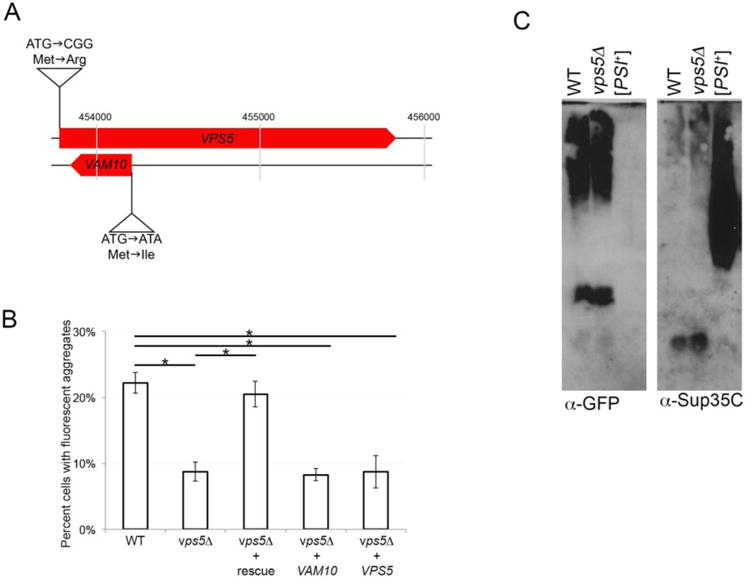
vps5Δ strains have reduced aggregate formation frequency, yet show no change in SDS-resistant oligomers. A. The VPS5 open reading frame (YOR069w) and VAM10 open reading frame (YOR068c) are located on chromosome 15 in the yeast genome. Site directed mutagenesis was performed to generate plasmids that contain a mutation in the initiator methionine of either VPS5 or VAM10. Two nucleotide substitutions replaced the initiation methionine with an arginine in the VPS5 open reading frame, while leaving the VAM10 open reading frame untouched. In a second plasmid, a single nucleotide substitution at the beginning of the VAM10 open reading frame leads to a mutation that changes methionine for isoleucine, while maintaining the same wildtype amino acid (serine) in the VPS5 sequence encoded by the opposite strand. All plasmids were sequenced in both directions to confirm the engineered mutation and the opposite open reading frame sequence. B. Plasmids containing wildtype versions of both genes (rescue), or mutated versions that maintain wildtype versions of only one gene (VAM10 or VPS5) were transformed into vps5Δ [PIN+] 74D-694 strains (Manogaran et al., 2011) along with a plasmid containing a copper inducible Sup35PrD-GFP allele. Sup35PrD-GFP was overexpressed for 24 hours in wildtype, vps5Δ, or vps5Δ strains with the indicated plasmid. The number of cells containing ring, line, or dot-like aggregates was counted from a population of at least 300 cells from three independent transformants. Standard deviation is shown. Statistically significant differences from wildtype or vps5Δ strains were determined by unpaired two-tailed t-test * p<0.005. C. Sup35PrD-GFP was overexpressed in wildtype and vps5Δ strains for 24 hours. Cultures were lysed and immediately subjected to SDD-AGE immunoblots using anti-GFP antibody (left) to detect Sup35PrD-GFP and anti-Sup35C antibody to detect full length Sup35p (BE4; right) according to Sharma et al., 2017. [PSI+] lysates are run for the detection of established [PSI+] oligomers.
