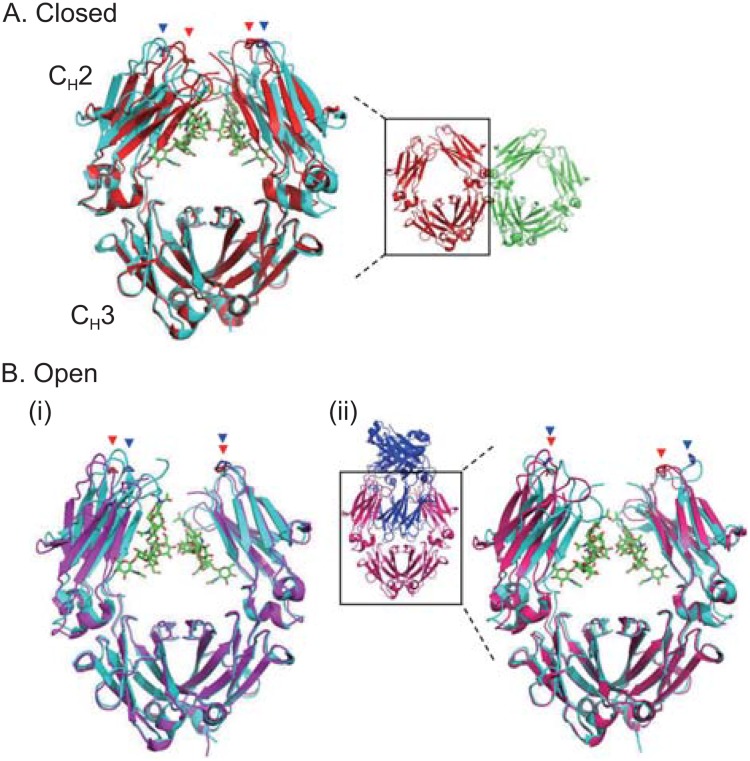
Figure 2.
Comparison of nonglycosylated and glycosylated Fc structures. (A) Closed conformation of the nonglycosylated Fc. Superposition of the E. coli-produced aglycosylated human IgG1-Fc (red) (PDB ID code: 3S7G) with the glycosylated human IgG1-Fc (cyan) (PDB ID code: 3AVE). Overall structure of the two aglycosylated Fc molecules is shown in red and green, and the Fc shown in red is superimposed with the glycosylated Fc. (B) Open conformation of the nonglycosylated Fcs. (i) Superposition of the enzymatically deglycosylated human IgG1-Fc (magenta) (PDB ID code: 3DNK) with the glycosylated human IgG1-Fc (cyan) (PDB ID code: 3AVE). (ii) Superposition of deglycosylated human IgG4-Fc myeloma protein Rea (pink) (PDB ID code: 4D2N) with the glycosylated IgG4-Fc (cyan) (PDB ID code: 4C54). Overall structure of the two interlocked Fc molecules is shown in pink and blue. The Fc shown in pink is superimposed with the glycosylated Fc. The Fc glycans are shown in green sticks. The Pro329 residues located in the FG loop of the CH2 domains are indicated by red and blue arrowheads for the nonglycosylated and glycosylated CH2 domains, respectively. The molecular models were produced with PyMOL (The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 1.8.5.0, Schrodinger, LLC)