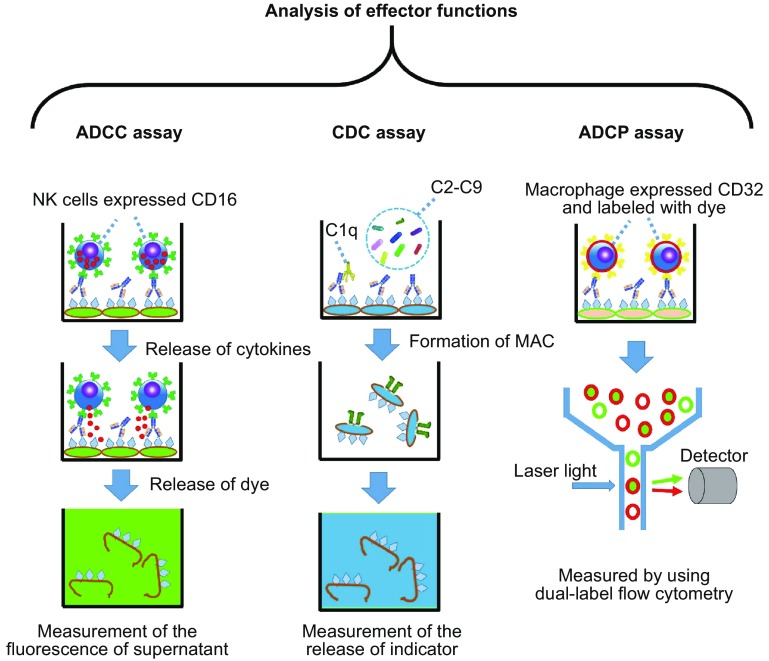
Figure 3.
Analysis of effector functions. For the ADCC assay (left panel), target cells are labeled with an indicator (such as calcein) and opsonized by using the test antibody at the indicated final concentration, effector cells (purified NK cells or peripheral blood mononuclear cells) are added in an appropriate ratio to target cells, and the final fluorescence intensity of the supernatant is measured. The procedure of the CDC assay (middle panel) is similar to the ADCC assay, except for the use of a complement to replace the effector cells. For the ADCP assay, target cells and the macrophage (differentiated by purified monocytes) were first labeled with fluorescent dyes and opsonized with the test antibody at indicated final concentration, after which the fluorescence was measured with a dual-label flow cytometry