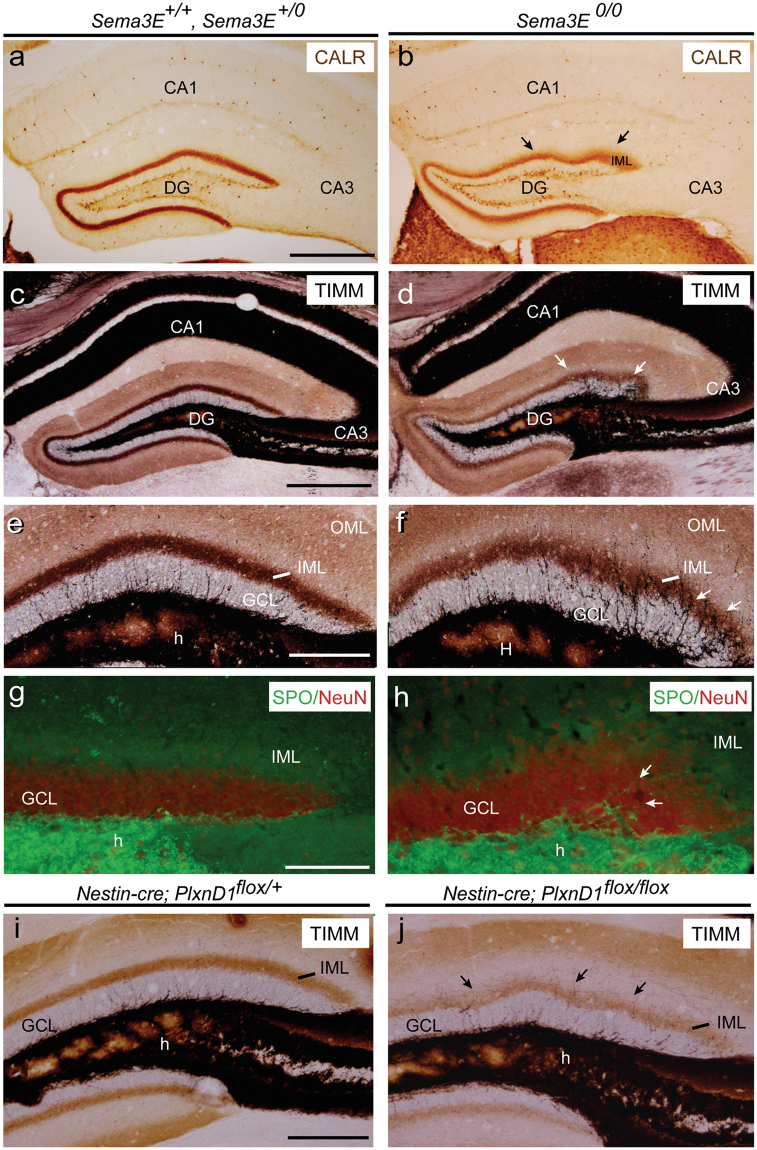
Figure 6.
(a,b) Examples of α-Calretinin immunostaining in the hippocampus proper and dentate gyrus of adult Sema3E+/+ and Sema3E+/0 (a) and Sema3E0/0 (b) mice. Note the presence of several waves in the IML of the suprapyramidal blade (arrows in b). (c–f) Photomicrographs illustrating the pattern of selenite-silver staining (TIMM) in Sema3E+/0 and Sema3E+/+ (c,e) and Sema3E0/0 (d,f) mice. Note the numerous ectopic mossy fibers crossing the granule cell layer entering the molecular layer of mutant mice (arrows in d,f). (g–h) Double immunolabeling of Synaptoporin (SPO, green) and NeuN (red) in the dentate gyrus of Sema3E+/+ and Sema3E+/0 (g) and Sema3E0/0 (h) mice showing ectopic mossy fibers crossing the granule cell layer in mutant mice (arrows in h). (i–j) High-power photomicrographs illustrating the pattern of selenite-silver staining (TIMM) in control (Nestin-cre; PlxnD1flox/+) and PlexinD1-deficient (Nestin-cre; PlxnD1flox/flox) mice. Abbreviations as in Figs 1–5 and CALR = calretinin; SPO = synaptoporin. Scale bar: a = 500 μm pertains to b; c = d = 500 μm. e = 150 μm pertains to (f,i–j); g = h = 100 μm.