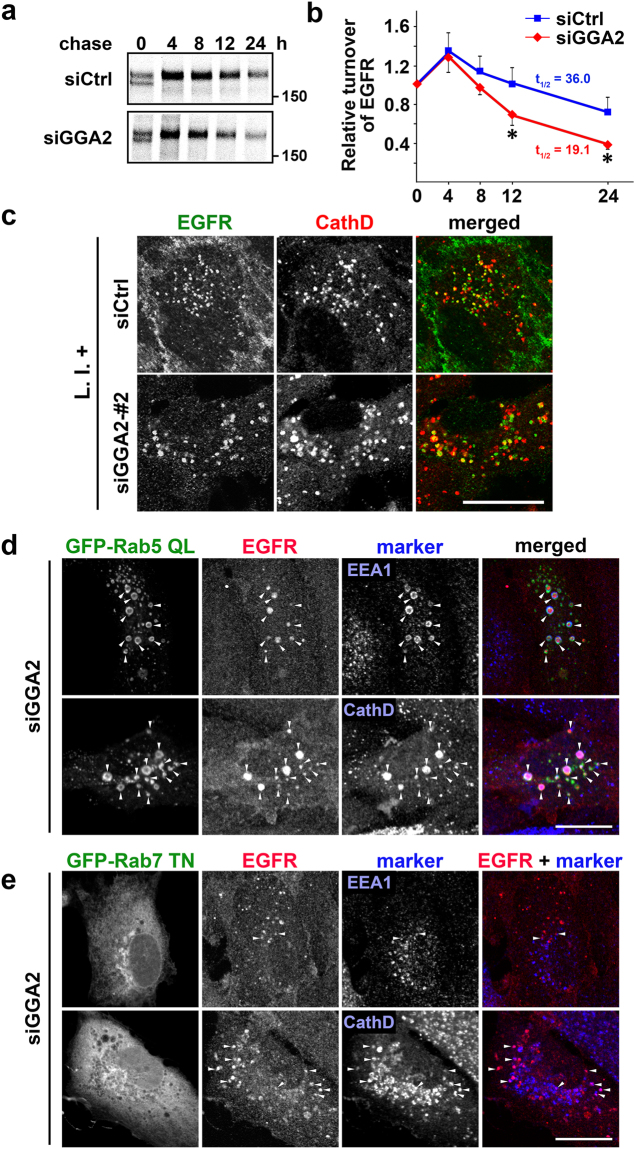
Figure 2.
GGA2-depletion facilitates lysosomal degradation of EGFR via post-Golgi compartments. (a) Control (siCtrl) and GGA2-depleted (siGGA2) ARPE-19 cells were pulse-labeled with [35S]-methionine and cysteine, and were chased for indicated periods. The cell lysates were then subjected to immunoprecipitation using anti-EGFR antibody as described in Materials and Methods. Uncropped gels are presented in Supplementary Fig. 6. (b) Signals for EGFR were quantified in three experiments and were plotted as means ± SD. Differences between siCtrl and siGGA2 at each time point were identified using Student’s t-test; *P < 0.05. (c) Control (siCtrl) and GGA2-depleted (siGGA2-#2) ARPE-19 cells were treated with lysosomal protease inhibitors (L.I.+) for 6 h, followed by fixation and double immunofluorescence staining with anti-EGFR (green) and anti-cathepsin D (red) antibodies; Bar, 20 μm. See Supplementary Fig. S2a for images of low magnification and alternative siRNA for GGA2. (d and e) GGA2 knockdown ARPE-19 cells transfected with GFP-Rab5 QL (d) or GFP-Rab7 TN (e) were double immunostained with antibodies for EGFR and EEA1, or EGFR and cathepsin D (CathD). Arrowheads indicate colocalization of three signals (d), or two signals of EGFR and either EEA1 or cathepsin D (e). Bars, 20 μm.