Figure 6.
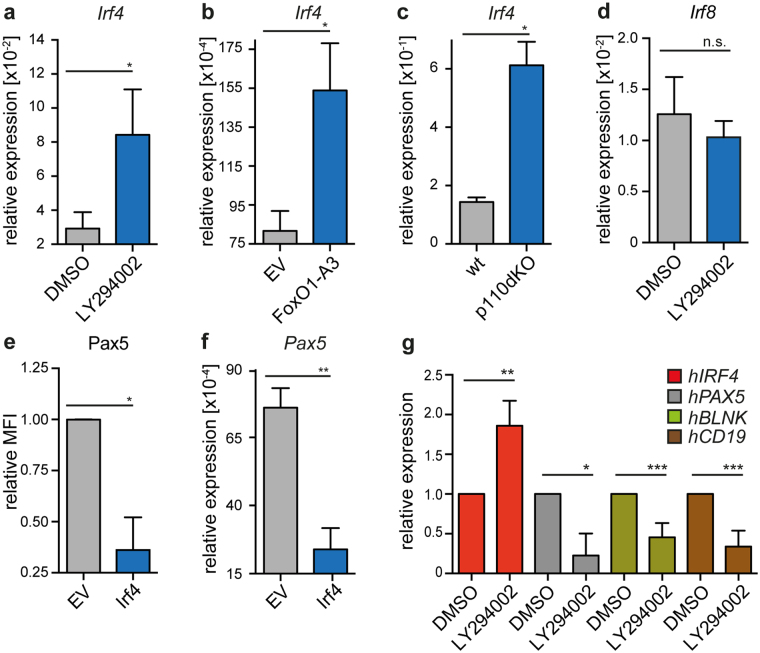
FoxO1 induces Irf4 to repress Pax5. (a) Total RNA from a SLP-65-deficient pre-B cell line, treated with LY294002 or DMSO for 12 h, was isolated. Hprt and Irf4 mRNA-levels were detected with specific primers by qRT-PCR using the SYBR-Green detection method (n = 5). (b) Cells from a bm-derived wt pre-B cell line were transduced with FoxO1-A3 or EV and at day 1 post transduction total RNA was isolated. Expression of Hprt and Irf4 mRNA-levels were detected by qRT-PCR using a SYBR-Green detection method (n = 3). (c) Total RNA from p110dKO and bm-derived wt pre-B cell lines was analyzed for Hprt and Irf4 transcript levels by qRT-PCR using the SYBR-Green detection method (n = 3). (d) Hprt and Irf8 mRNA-levels were detected in RNA from Fig. 6a with specific primers by qRT-PCR using the SYBR-Green detection method (n = 5). (e) Similar to FoxO1-A3 in Fig. 5b, cells from a bm-derived wt pre-B cell line were transduced with Irf4 or EV and Pax5 expression was analyzed at day 2 after transduction by intracellular FACS. (f) Total RNA of cells from Fig. 6e was isolated to analyze transcript levels of Pax5. Hprt and Pax5 mRNA-levels were detected by qRT-PCR using the SYBR-Green detection method (n = 3). (g) Human mature B cells from peripheral blood were isolated, treated with LY294002 and analyzed for IRF4, PAX5, BLNK and CD19 transcripts (n = 3). Results are shown as mean ± SD, run as duplicates. Data are representative of 2 (c) or at least 3 (a,b, d–g) independent experiments. Statistical significance was calculated using the t-Test.