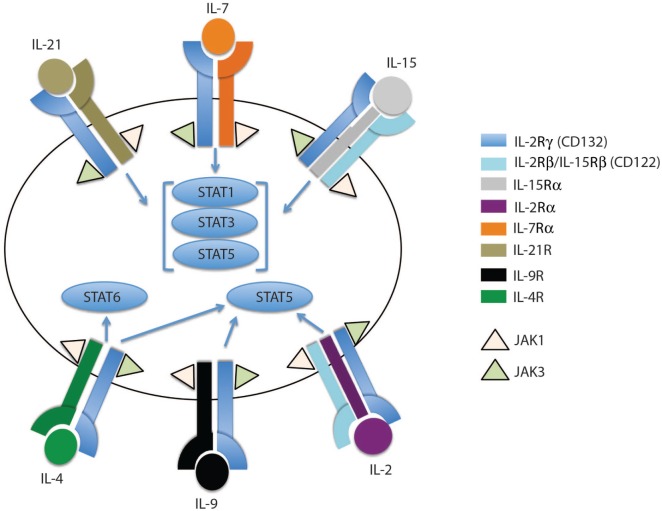
Figure 1.
The family of common gamma chain cytokines and their receptors. The common gamma chain cytokine receptors are depicted in this cartoon showing IL-2Rγ (CD132) as the common subunit in all the receptors. Each receptor has its unique subunit that forms a heterodimer or heterotrimer receptor complex with the common gamma chain subunit. IL-4R, IL-7Rα, IL-9R, and IL-21R subunits dimerize with the common gamma chain subunit to form heterodimers that bind IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, and IL-21 cytokines, respectively. IL-2 and IL-15 receptors share two subunits, IL-2Rγ and IL-2Rβ, which trimerize with IL-2Rα or IL-15Rα to form the IL-2 or IL-15 receptor complex, respectively. The binding of each cytokine to its receptor complex results in phosphorylation of JAK1 and JAK3. The activated JAKs activate different STAT members, which then migrate to the nucleus to induce or inhibit expression of specific target genes.