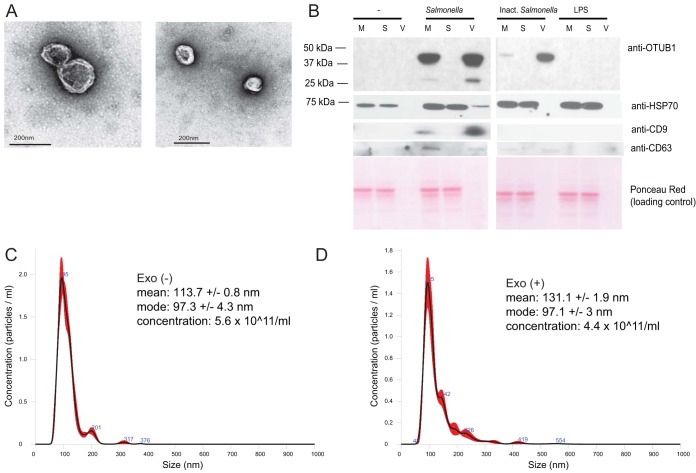
FIG 6.
Exosomes produced by macrophages infected with S. Typhimurium at 2 hpi. THP-1 macrophages were left uninfected or infected with wild-type viable or paraformaldehyde-inactivated S. Typhimurium (Inact. Salmonella). Alternatively, the cells were treated with S. Typhimurium-derived LPS. Cell culture supernatants were collected 2 hpi and subjected to serial centrifugation to isolate exosomes. (A) Exosomes derived from S. Typhimurium-infected macrophages were visualized by transmission electron microscopy. (B) Cell culture medium (M), vesicle-free supernatant (S), and the extracellular vesicle fraction (V) were analyzed by Western blotting to show the presence of OTUB1, HSP70, CD63, and CD9 in the exosomes. Ponceau Red was used to stain protein material, and HSP70, CD63, and CD9 were used as exosome markers. (C and D) Size distribution of exosomes produced by THP-1 macrophages at 2 hpi. THP-1 macrophages were left uninfected (C) or were infected with wild-type S. Typhimurium (D). Exosomes were purified at 2 hpi from the cell culture supernatant by serial centrifugation. The mean and mode sizes of the exosomes (nm) and the concentrations of exosomes (number of particles/ml) were recorded by NanoSight. Exo(+), exosomes derived from infected macrophages; Exo(−), exosomes derived from uninfected macrophages.