FIG 2.
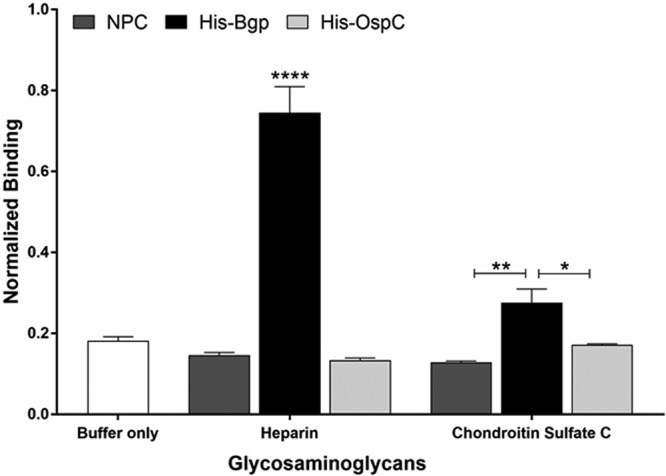
Bgp is a GAG-binding adhesin with affinity for heparin. Biotinylated GAGs were able to bind to recombinant Bgp protein (20 μg/ml), with the most-significant adherence to heparin. Bgp binds poorly to chondroitin sulfate C. Recombinant OspC was included as a negative control. The no-protein control (NPC) shows that interaction of Bgp was specific for GAGs. Each bar represents the mean ± standard deviation (SD) for quadruplicate samples. Data were normalized by dividing the total absorbance obtained in each well by the coated protein concentration in parallel control wells as determined by ELISA. The adjusted binding was then averaged for four replicates per treatment, and the percentage of biotinylated GAGs bound to the respective proteins is shown. Statistical significance (****, P ≤ 0.0001; **, P ≤ 0.01; *, P ≤ 0.05) was determined by the Student t test for comparison of samples with unequal variances.
