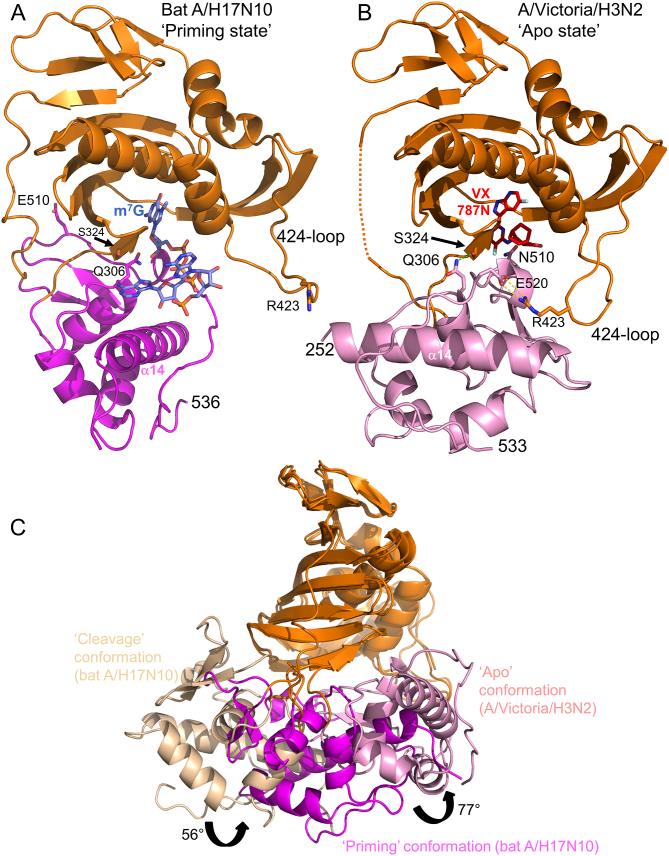
Figure 4.
Three different configurations of the cap-midlink double domain. (A) ‘Priming’ conformation. The juxtaposition of the midlink (magenta) and cap-binding (orange) domains as observed in the H17N10 capped RNA (blue sticks) complex (Figure 1B). The location of the three VX-787 resistance mutations, Gln306, Ser324 and Asn510 is shown as well as Arg423 in the 424-loop which makes a salt bridge with PB1 Glu277 (not shown)(compare (B) and see text). (B) ‘Apo’ conformation of A/H3N2 midlink (pink) and cap-binding (orange) domains as observed in the double domain structure with bound VX-787N (red sticks). The location of the three VX-787 resistance mutations, Gln306, Ser324 and Asn510 is shown as well as the salt-bridge of Arg423 in the 424-loop with Glu520 (compare (A) and see text). A very similar configuration of the two domains has already been reported for A/H5N1 with bound m7GTP (PDB: 5FMM, root-mean-square deviation of 0.95 Å for 276 superposed Cα atoms) and for influenza B polymerase (PDB: 5EPI) (16). (C) Superposition by means of the cap-binding domain (orange) of the ‘cleavage’, ‘priming’ and ‘apo’ configurations of the midlink (respectively wheat, magenta and pink) and cap-binding double domain with the respective rotation angles marked.