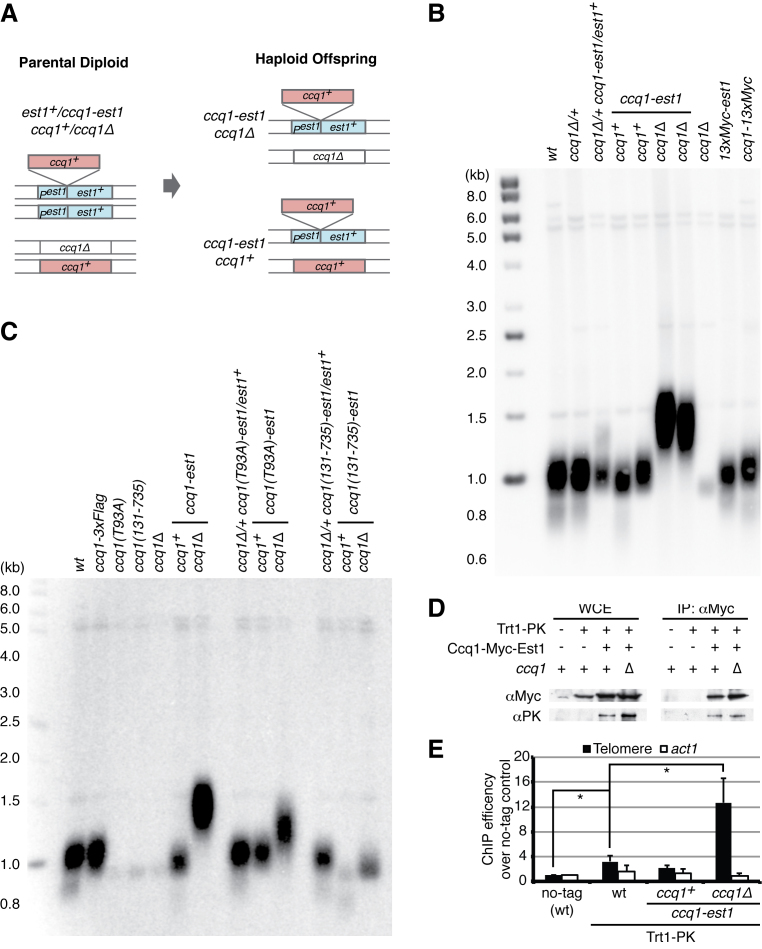
Figure 2.
The Ccq1-Est1 fusion bypasses the recruitment step. (A) Schematic diagram of the fusion system. The ccq1 gene sequence with thirteen tandem myc sequences was inserted after the start codon of one est1 allele in a diploid strain heterozygous for ccq1Δ. Expression of the intact chimera gene product (Ccq1–13xMyc-Est1) through the endogenous est1 promoter was confirmed using anti-Myc antibody (Supplementary Figure S3). After sporulation, haploids were obtained which expressed the chimera protein from the est1 locus in a ccq1Δ or ccq1+ background. (B) Telomere Southern blot shows that expression of the Ccq1-Est1 fusion protein leads to longer telomere maintenance in the absence of endogenous Ccq1. 13xMyc epitope tagging to N-terminus of Est1 and the C-terminus of Ccq1 did not impair function in telomere length homeostasis. (C) Telomere Southern blot shows that the Ccq1-Est1 chimera bypasses need for phosphorylation at Ccq1 Thr93 for telomere maintenance but truncation of Ccq1 N-terminus (131–735) leads to maintenance of short telomeres. In the presence of the Ccq1(131–735)-Est1 chimera, telomere lengthening was severely impaired in ccq1+ background. Nevertheless, elongation of telomeres was observed in the ccq1Δ background, suggesting that negative regulation by endogenous Ccq1 remains functional. (D) Co-immunoprecipitation with the Ccq1–13xMyc-Est1 chimera shows stable association with Trt1. (E) Chromatin immunoprecipitaion (ChIP) with the PK epitope-tagged Trt1 shows efficient recruitment of telomerase to telomeres in the presence of the Ccq1-Est1 chimera and the absence of endogenous Ccq1. DNA fragments containing telomere-adjacent sequence and the act1 gene (as internal control) were detected by quantitative PCR. ChIP efficiencies of telomeric DNA and act1 were calculated against input (whole cell extract), and the fold enrichment over no-tagged negative control is expressed. Mean average of three biological replicas is shown. Significant differences over Trt1-PK (wild type) are indicated as asterisks (two-tailed t-test: *P < 0.05).