Figure 6.
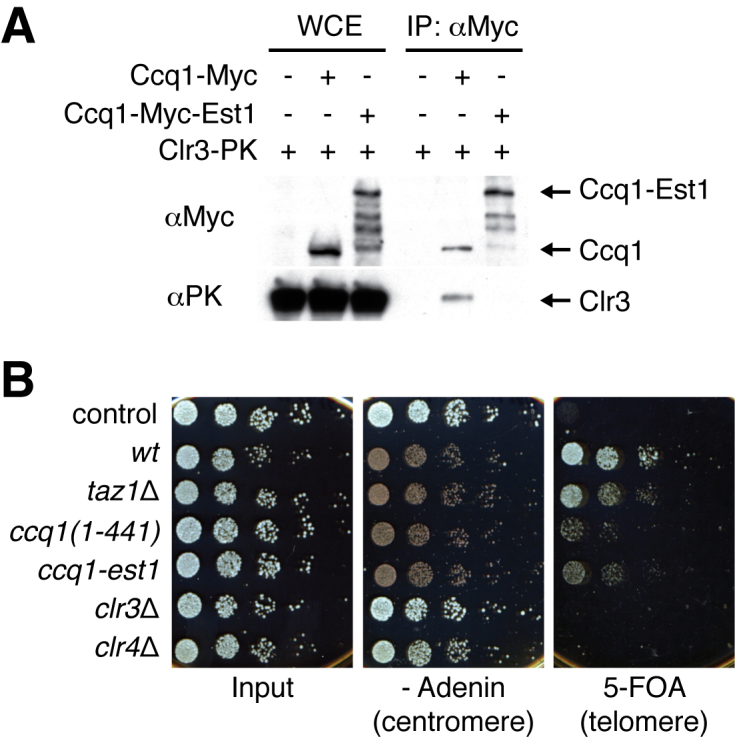
Clr3 associates with Est1-unbound Ccq1 and represses telomere-adjacent transcription. (A) Clr3 was co-immunoprecipitated with the Myc-epitope tagged Ccq1 but not with the Ccq1-Est1 chimera (in ccq1Δ background). Presence of endogenous Est1-free Ccq1 further reduced the interaction between Clr3 and the Ccq1-Est1 chimera (Supplementary Figure S10). (B) The heterochromatic gene-silencing assay. Serial dilution spot assay to measure transcription efficiencies of genes inserted at the centromere and telomere. The wild type ade6+ gene cassette was inserted at a centromeric outer repeat region of chromosome 1, and the wild type ura4+ gene cassette was inserted at the telomere on the left arm of chromosome 2. Centromeric repression of the ade6+ gene leads to a growth defect and red colouring, and telomeric repression of the ura4+ gene leads to survival of cells under 5-FOA treatment. Control cells are prototrophic, expressing both Ade6 and Ura4 (lane 1). The taz1 deletion or ccq1(1–441) truncation mutation leads to activation of telomeric transcription, whereas deletion of clr3 or clr4 leads to gene silencing defects at both telomeres and centromeres.
