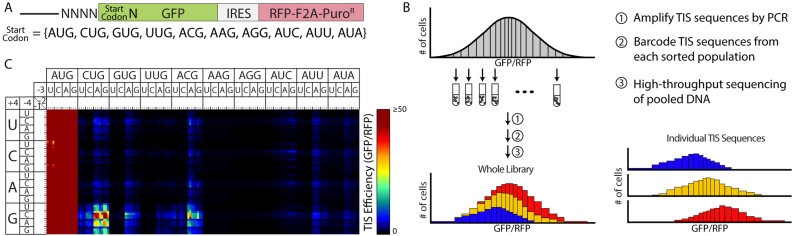
Figure 1.
High-throughput analysis of TIS motifs utilizing non-AUG start codons. A) The TIS reporter used to measure translation initiation efficiency from every AUG and non-AUG start codon. The -4 to -1 and +4 positions were varied to create a library of all possible sequences at those positions (N = A, C, G, or U). RFP was expressed from the same transcript using an internal ribosome entry site (IRES) and served to normalize GFP expression. F2A is a peptide that allows multiple proteins to be expressed from a single open reading frame. PuroR is the puromycin resistance gene, which enabled selection of stably transduced cells. B) Summary of the FACS-seq method. A population of stably transduced cells is sorted into 20 equally populated gates based on TIS efficiency (GFP/RFP). The TIS sequences are then PCR-amplified and barcoded before being pooled and sequenced. FACS-seq histograms were then created for each TIS sequence based on the number of reads for each TIS in each gated population. The median efficiency values for each TIS sequence were then fit with a generalized linear model that accounted for important dinucleotide interactions. C) Heat map of the TIS efficiencies measured via FACS-seq. The labels of the nucleotides at the -2 and -1 positions follow the same pattern as the other positions: U, C, A, G. A TIS efficiency of 100 corresponds to the TIS sequence CACCAUGG.