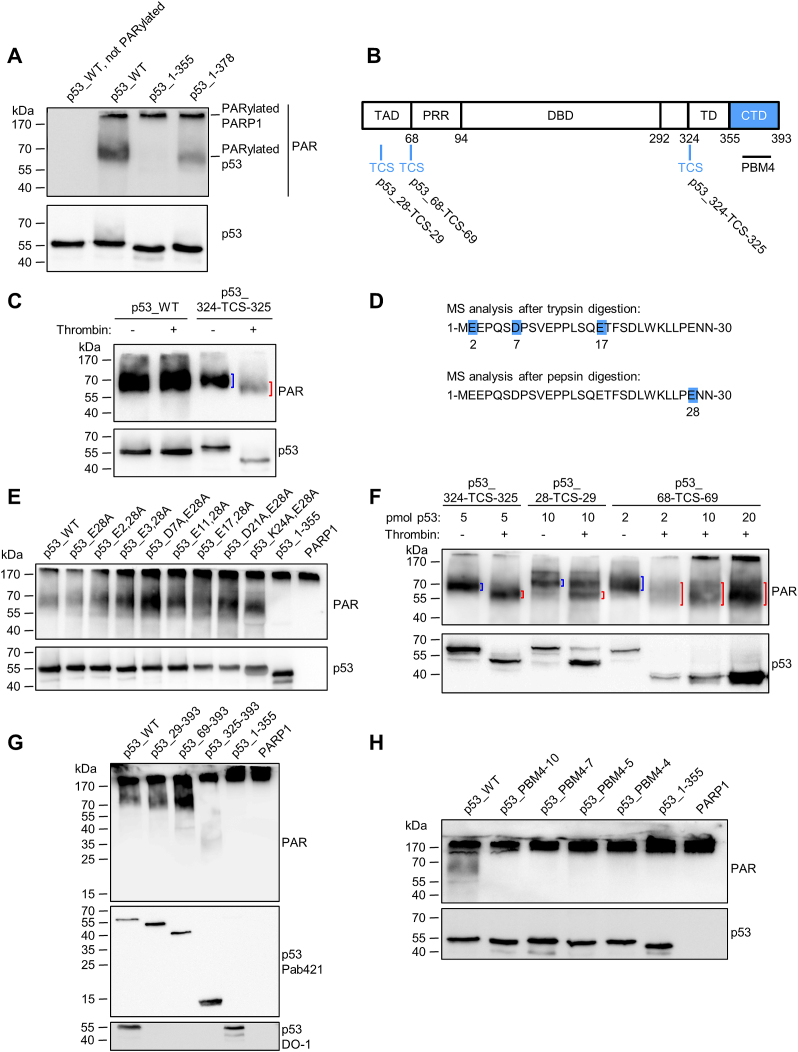
Figure 4.
The CTD of p53 is essential for covalent PARylation of p53. (A) In-vitro PARylation assay to test covalent PARylation of C-terminally truncated versions of p53. (B) Schematic representation of the here used human p53 protein variants containing a thrombin cleavage site (TCS). (C) Thrombin cleavage assay with covalently PARylated p53_324-TCS-325. Down-shifted bands are indicated by red brackets, bands of non-thrombin-treated samples by blue brackets. (D) Mass spectrometric identification of covalent PARylation sites in p53_WT. PDE I –treated PARylated p53 was trypsin or pepsin digested. (E) In-vitro PARylation assay with p53 containing mutations at the PARylation sites identified in (D). PARP1: A control PARylation reaction was performed in the absence of p53 variants. (F) Thrombin cleavage assay with covalently PARylated p53_28-TCS-29 or p53_68-TCS-69. (G) In-vitro PARylation assay with N-terminally truncated versions of p53. (H) In-vitro PARylation assay with p53-PBM4 mutants. Exchanges of 10, 7, 5 or 4 aa were introduced into the CTD (protein sequences are shown in Figure 2B).