Fig. 1.
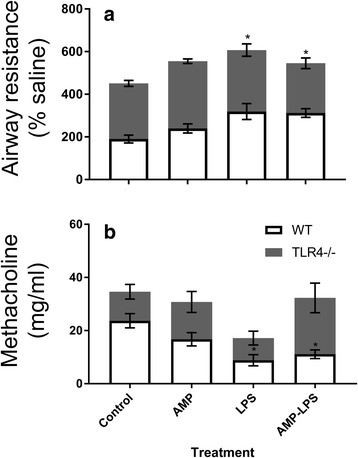
Airway resistance (a) and sensitivity to methacholine at 30 mg/ml (b) for wildtype (WT) and mice not expressing TLR4 (TLR4−/−) for each treatment. Airway resistance (Raw) values for the largest methacholine challenge (MCh, 30 mg/ml) are presented as a percentage of the initial saline challenge given to each animal given prior to commencing MCh challenges (a). Raw was augmented in WT mice treated with nebulized LPS and AMP-LPS only. Airway sensitivity was calculated by interpolating the amount of MCh needed to cause a doubling of baseline responses (b). WT mice treated with LPS and AMP-LPS required significantly less MCh than that needed for control mice, indicating more sensitive airways due to LPS and AMP-LPS treatments in the presence to TLR-4 (*p < 0.05 compared to controls). No significant differences were observed in airway resistance or sensitivity between treatments of LPS or AMP-LPS within each mice strain (p > 0.05)
