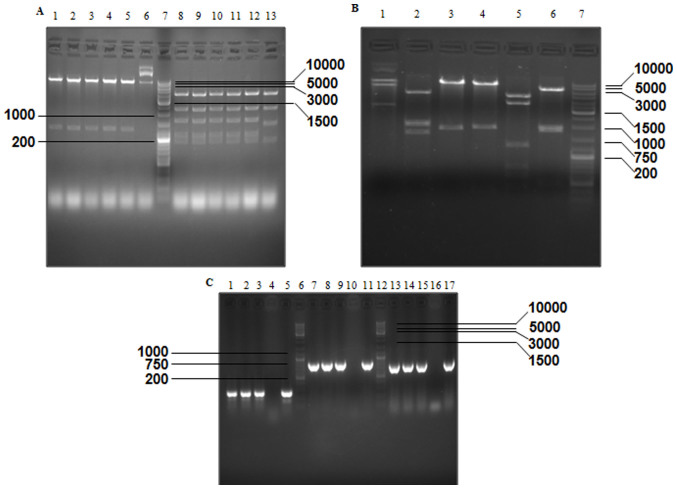
Figure 3.
Verification of PCA19-Gp53 and p74-Tp-Gp53 plasmids by gel electrophoresis, according to the size (bp) of excised fragments. (A) Excised fragments of PCA19-Gp53 detected by gel electrophoresis. Lanes 1–6, double digestion with EcoRI and SalI; lane 7, GeneRuler™ DNA Ladder mix (10,000 bp); lanes 8–13, digestion with PvuII. (B) Excised fragments of P74-Tp-Gp53 detected by gel electrophoresis. Lanes 1–6, digestion of PCA19-Gp53 by BglII, SacI and XbaI, NcoI and SalI, BamHI, PstI and NcoI, respectively; and lane 7, GeneRuler™ DNA Ladder Mix (10,000 bp). (C) DNA fragments of Ad-Tp-E1A-Gp-p53 were detected by gel electrophoresis. Lanes 1–3, amplification of Ad-Tp-E1A-Gp-p53 using the GT154+GT156 primer; lanes 4, 10 and 16, negative control; lane 5, amplification of plasmid P74-TP using the GT154+GT156 primer; lanes 6 and 12, GeneRuler™ DNA Ladder Mix; lanes 7–9, amplification of Ad-Tp-E1A-Gp-p53 using the W267+W268 primer; lane 11, amplification of plasmid PENTER-p53 using the W267+W268 primer; lanes 13–15, amplification of Ad-Tp-E1A-Gp-p53 using the W331+W332 primer; and lane 17, amplification of plasmidpGL3-GFAP by using the W331+W332 primer. E1A, early viral 1A; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein.