Figure 5.
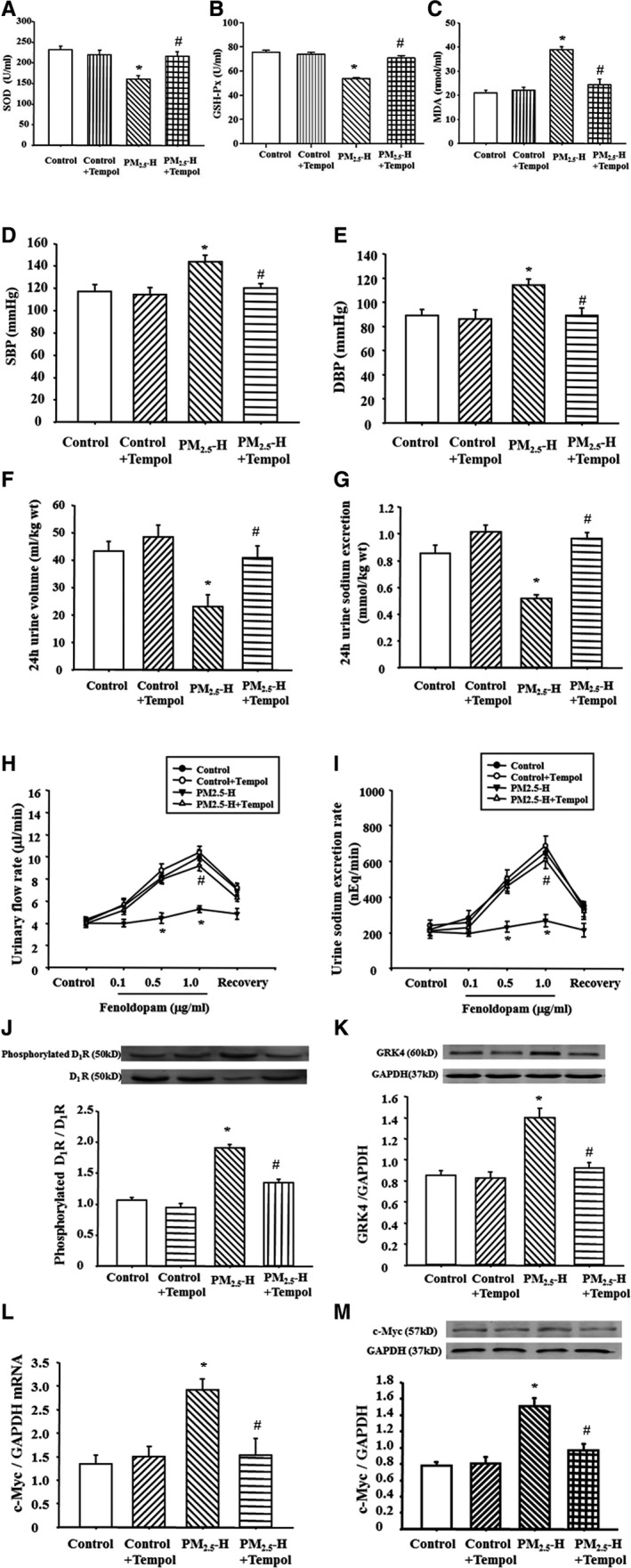
Effect of tempol on blood pressure and sodium excretion in Sprague‐Dawley (SD) rats exposed to fine particulate matter (PM 2.5). SD rats exposed to PM 2.5 were treated with tempol for 3 weeks. Plasma superoxide dismutase (SOD) (A), glutathione peroxidase (GSH‐Px) (B), and malondialdehyde (MDA) (C) levels were checked in those rats (n=12 in each group). The blood pressure (D and E) and sodium excretion (F and G) were recorded (n=12 in each group). Moreover, the fenoldopam‐mediated urinary flow rate (H) and urine sodium excretion rate (I), G‐protein–coupled receptor kinase 4 (GRK4) expression (J), and dopamine D1 receptor (D1R) phosphorylations (K), as well as c‐Myc mRNA (L) and protein expressions (M) were checked (n=10 in each group). DBP indicates diastolic blood pressure; PM2.5‐H, 30 μg PM 2.5 per time; and SBP, systolic blood pressure. *P<0.0001 vs control rats, # P<0.0001 vs PM 2.5‐H rats.
