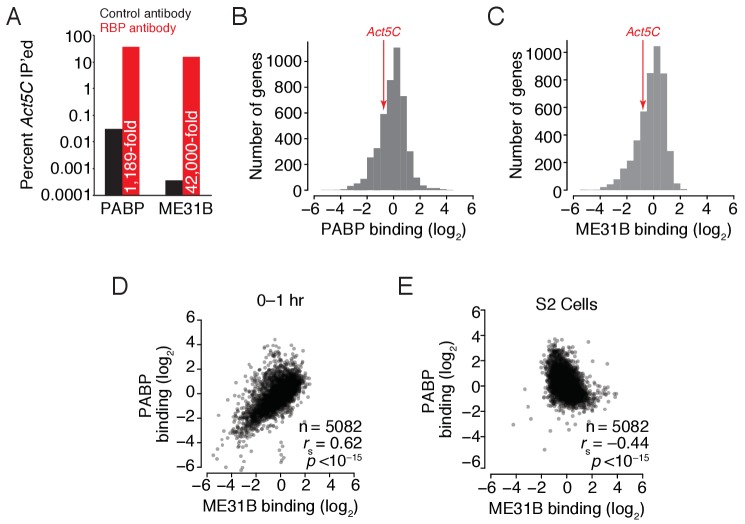
Figure 2. ME31B and PABP bind similar mRNAs in 0–1 hr embryos.
(A) Enrichment of Act5C transcripts in PABP and ME31B immunoprecipitations. Extracts from 0 to 1 hr embryos were immunoprecipitated with the indicated antibodies (control pull-downs, black; PABP or ME31B pull-downs, red). In the case of PABP, complexes were immunoprecipitated with Fab1; ME31B was precipitated from eGFP-ME31B embryos with anti-GFP antibodies. The percent of Act5C mRNA pulled down was quantified by RT-qPCR, primed by oligo(dT) (in the case of PABP) or random-hexamers (in the case of ME31B). Numbers reflect the fold enrichment of Act5C in PABP or ME31B immunoprecipitations relative to the control immunoprecipitations. (B) Distribution of PABP enrichment values transcriptome-wide, as determined by RIP-seq. For mRNAs of each gene that satisfied the expression cut-offs, PABP binding was calculated. Highlighted is the binding for Act5C. (C) As in (B), except for ME31B binding values. (D) Comparison of PABP and ME31B binding in 0–1 hr embryos. (E) Comparison of PABP and ME31B binding in S2 cells.