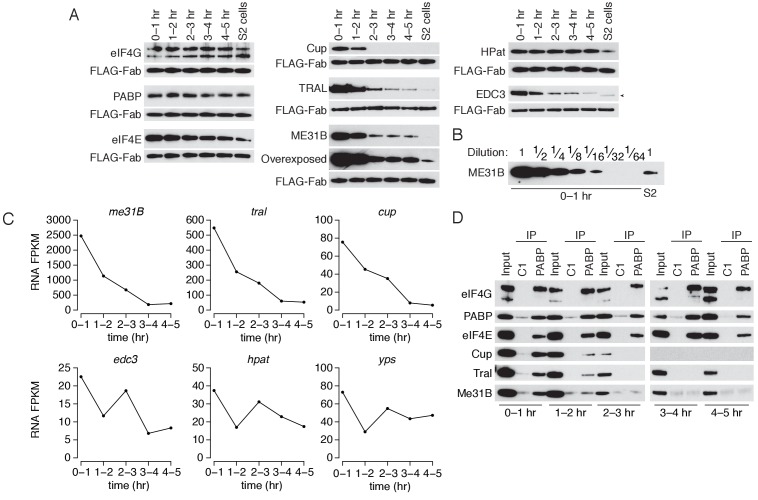
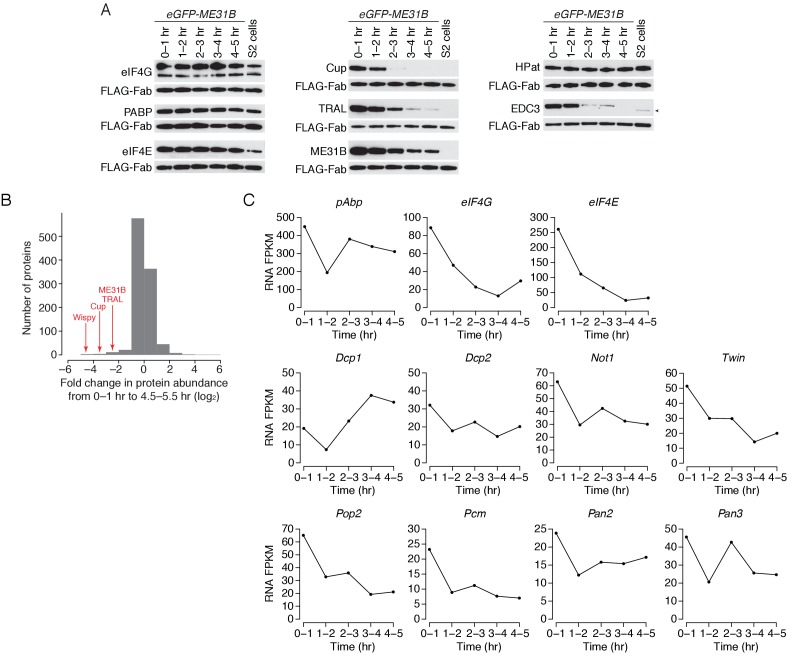
Figure 4. The levels of ME31B, TRAL, and Cup are developmentally regulated through multiple mechanisms.
(A) Western blot analysis of protein abundance over the first five hours of development. Extracts from embryos harvested at one-hour intervals and from S2 cells were collected, and constant amounts of exogenous FLAG-tagged Fabs were added to each lysate. Western blot analysis of the indicated proteins is shown. The arrowhead indicates a nonspecific band. (B) Levels of ME31B in 0–1 hr embryos relative to S2 cells. Western blot of serial dilutions of 0–1 hr embryo extracts and undiluted S2 cell lysate was probed for ME31B. (C) Analysis of mRNA levels over the first five hours of development. RNA-seq was used to analyze RNA abundance in embryos harvested at one-hour intervals. Libraries were prepared with rRNA-depletion. Shown are the FPKM values for the indicated genes. (D) Analysis of the interaction between PABP and Cup, TRAL, and ME31B in early development. Extracts from embryos at the indicated time points were immunoprecipitated with control C1 or anti-PABP Fabs. Western blots of inputs and immunoprecipitates were probed using the indicated antibodies.