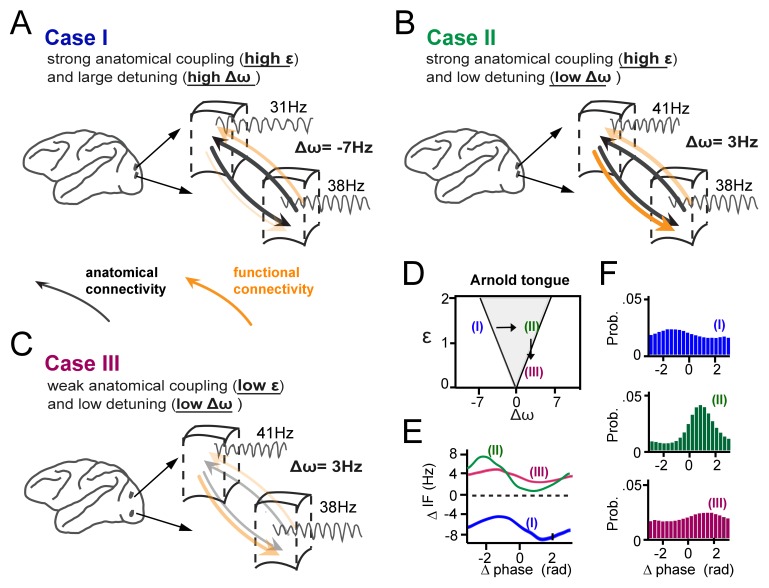
Figure 9. Summary of the main findings.
(A-C) Three cases of cortical gamma-band interactions are used for illustration (A) In case I, two cortical locations have strong anatomical connections (black thick arrows, high interaction strength ε) and a large detuning Δω. This results in low functional interaction (orange arrows). (B) In case II, anatomical connections are as high as in (A), but detuning is low. This leads to strong functional interactions. The location with higher frequency functionally dominates the location with lower frequency. (C) In case III, there is the same low detuning as in (B), but with low anatomical connectivity. This results again in low functional interaction. (D) The three cases represented in relation to the Arnold tongue. Only case II is within the Arnold tongue. Moving out of the Arnold tongue by a change in Δω (from II to I) or a change in ε (from II to III) strongly reduces synchronization. (E) The instantaneous frequency difference modulations (ΔIF(θ)) as a function of phase-difference for the three examples. (F) The corresponding phase-difference probability distributions.