FIGURE 2. VSL#3 increased TCPTP enzymatic activity in T84 intestinal epithelial cells.
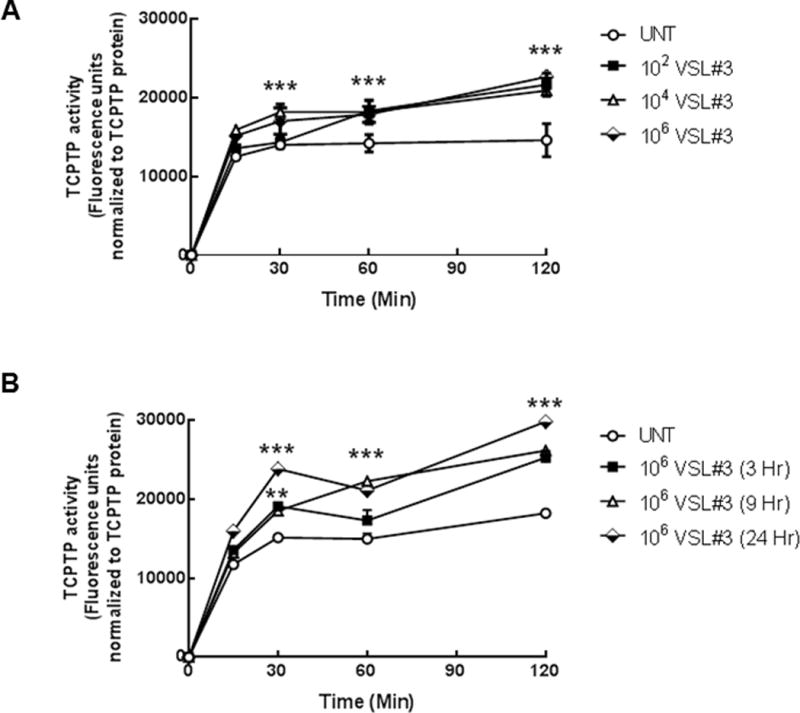
(A) T84 cell monolayers were treated with VSL#3 at varying concentrations (102, 104, 106 CFU/mL) for 9 hrs. TCPTP was immunoprecipitated from whole cell lysates and TCPTP activity was assessed over 120 minutes (n = 5). A sample from each immunoprecipitation was run on an SDS-PAGE gel and following transfer to PVDF membrane, probed for TCPTP to confirm equal protein loading. Fluorescence activity units were expressed relative to TCPTP protein levels to account for any differences in overall phosphatase amounts. 106 CFU/mL induced the greatest increase in TCPTP enzymatic activity (p<0.001, n=5). (B) A time course of incubation of T84 cells with 106 CFU/mL was performed for 3, 9 and 24 hrs. VSL#3 maximally increased activity above untreated controls after 9 hr incubation (p<0.001; n=4). All data are expressed as a percentage of the control ± SEM and analyzed by ANOVA and Student-Newman-Keuls post-hoc test. Asterisks denote significant differences vs. the respective untreated control. (***,p< 0.001 compared to the respective untreated time point).
