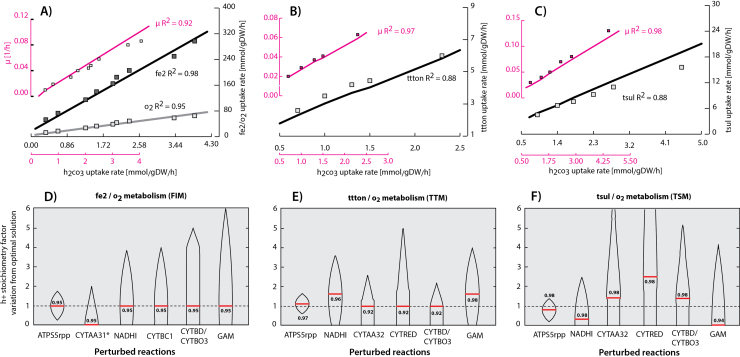
Fig. 2.
Parameter estimation and validation of the carbon fixation and electron donor pathways results: based on the genetic algorithm model parameter estimation results, three graphs representing the experimental phenotypic data (represented in squares) and the model-predicted growth conditions (represented in lines) on ferrous ion (A), tetrathionate (B) and thiosulfate (C) as electron donors and using oxygen as an electron acceptor are shown. The corresponding R2Set (1:fe2, 2:ttton and 3:tsul) for each predicted/experimental dataset pair are shown. A R2Set sensitivity analysis for ferrous ion (D), tetrathionate (E) and thiosulfate (F) metabolism was performed. Proton translocation predicted stoichiometry values were varied along the y axis and the corresponding R2Set variation from the optimum was calculated and plotted each one of the proton translocated stoichiometry predicted reactions as a violin graph. In this case R2Set represents the prediction error for each studied metabolism independently. The maximum calculated R2Set due to parameter variations was reported and represented as a red line. For sake of simplicity GAM denotes the stoichiometry on the atp reaction consumption in the BOF due to growth associated maintenance. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)